Volumetric Medical Data Visualization in 2025: How 3D Imaging is Transforming Healthcare Diagnostics and Treatment. Explore the Next Wave of Innovation, Market Expansion, and Clinical Impact.
- Executive Summary: Key Trends and Market Drivers in 2025
- Market Size and Forecast (2025–2030): Growth Projections and CAGR Analysis
- Technological Innovations: Advances in 3D and 4D Visualization
- Leading Companies and Solutions: Profiles and Strategic Initiatives
- Clinical Applications: From Radiology to Surgery and Beyond
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
- Regulatory Landscape and Standards: Compliance and Interoperability
- Challenges and Barriers: Data Management, Security, and Adoption
- Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Emerging Markets
- Future Outlook: Next-Generation Visualization and Market Opportunities
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: Key Trends and Market Drivers in 2025
Volumetric medical data visualization is undergoing rapid transformation in 2025, driven by advances in imaging modalities, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud-based collaboration. The sector is witnessing a convergence of high-resolution 3D imaging, real-time rendering, and advanced analytics, enabling clinicians to interpret complex datasets with unprecedented clarity and speed. These trends are reshaping diagnostics, surgical planning, and patient engagement across radiology, oncology, cardiology, and neurosurgery.
A primary driver is the proliferation of next-generation imaging systems, such as multi-detector computed tomography (CT), high-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET), which generate vast volumes of data. Leading manufacturers like Siemens Healthineers, GE HealthCare, and Canon Medical Systems are integrating advanced visualization suites directly into their platforms, offering clinicians seamless access to volumetric reconstructions and interactive 3D models at the point of care.
AI-powered visualization is another key trend, with companies such as Philips and Siemens Healthineers embedding deep learning algorithms to automate segmentation, highlight anomalies, and generate predictive insights from volumetric datasets. These tools are reducing interpretation times and supporting more precise, personalized treatment planning. The integration of AI is also facilitating the transition from 2D slice-based review to immersive 3D and even 4D (time-resolved) visualization, enhancing the detection of subtle pathologies and improving surgical outcomes.
Cloud-based platforms are enabling remote access, multidisciplinary collaboration, and scalable storage for large volumetric datasets. Companies like GE HealthCare and Philips are expanding their cloud offerings, allowing clinicians to share interactive 3D models securely across institutions and devices. This is particularly relevant for telemedicine, tumor boards, and global health initiatives, where rapid, collaborative decision-making is essential.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see further integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) into clinical workflows. Firms such as Siemens Healthineers and Philips are piloting AR/VR solutions for preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation, aiming to improve surgical precision and patient outcomes. Regulatory support for digital health innovation and growing demand for minimally invasive procedures are likely to accelerate adoption.
In summary, the volumetric medical data visualization market in 2025 is characterized by technological convergence, AI-driven automation, and cloud-enabled collaboration. These trends are poised to drive significant improvements in diagnostic accuracy, workflow efficiency, and patient care over the coming years.
Market Size and Forecast (2025–2030): Growth Projections and CAGR Analysis
The volumetric medical data visualization market is poised for robust growth between 2025 and 2030, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced imaging modalities, the proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, and the growing demand for precision diagnostics. Volumetric visualization—encompassing 3D and 4D rendering of medical imaging data from modalities such as CT, MRI, and PET—enables clinicians to interpret complex anatomical structures with greater accuracy, supporting improved diagnostic and surgical outcomes.
Key industry players are investing heavily in research and development to enhance visualization software and hardware capabilities. Siemens Healthineers continues to expand its portfolio of 3D and 4D imaging solutions, integrating AI-driven features for automated segmentation and real-time rendering. GE HealthCare is similarly advancing its Edison platform, which leverages cloud-based analytics and visualization tools to streamline radiology workflows. Philips is focusing on interoperability and cloud deployment, enabling collaborative review of volumetric data across care teams.
The market’s expansion is further supported by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, which necessitate advanced imaging for early detection and treatment planning. The integration of volumetric visualization into surgical navigation systems and interventional radiology is also accelerating adoption, as real-time 3D guidance becomes standard in complex procedures. Additionally, the shift toward cloud-based and remote visualization platforms is expected to broaden access, particularly in underserved regions.
From 2025 to 2030, the volumetric medical data visualization market is projected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the high single digits to low double digits, reflecting both technological innovation and expanding clinical applications. North America and Europe are anticipated to maintain leading market shares due to established healthcare infrastructure and early technology adoption, while Asia-Pacific is expected to exhibit the fastest growth, driven by healthcare modernization and increasing investment in digital health.
- Continued R&D by Siemens Healthineers, GE HealthCare, and Philips will drive product innovation and market penetration.
- Cloud-based solutions and AI integration are set to become standard features, enhancing accessibility and diagnostic accuracy.
- Regulatory support for digital health and interoperability standards will further catalyze market growth.
Overall, the outlook for volumetric medical data visualization is highly positive, with sustained investment and technological progress expected to unlock new clinical and operational value across the global healthcare landscape.
Technological Innovations: Advances in 3D and 4D Visualization
Volumetric medical data visualization is undergoing rapid transformation in 2025, driven by advances in 3D and 4D imaging technologies. These innovations are reshaping diagnostic workflows, surgical planning, and patient engagement by enabling clinicians to interact with complex anatomical data in unprecedented ways.
A key trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with volumetric visualization platforms. AI-powered segmentation and reconstruction algorithms now allow for faster and more accurate rendering of 3D and 4D datasets from modalities such as CT, MRI, and ultrasound. For example, Siemens Healthineers has introduced AI-based tools within its syngo.via platform, enabling automated organ segmentation and dynamic visualization of moving structures, such as the beating heart, in real time. Similarly, GE HealthCare continues to expand its Edison platform, leveraging deep learning to enhance volumetric image clarity and reduce manual post-processing time.
Another significant development is the adoption of extended reality (XR) technologies—including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR)—for immersive visualization of volumetric data. Philips has advanced its IntelliSpace Portal with VR capabilities, allowing clinicians to explore 3D reconstructions interactively, which is particularly valuable for preoperative planning and patient education. Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 is increasingly used in surgical settings, enabling overlay of 3D anatomical models onto patients during procedures, thus improving precision and outcomes.
Cloud-based solutions are also gaining traction, facilitating collaborative review and analysis of volumetric datasets across institutions. Canonical and other cloud infrastructure providers are supporting secure, scalable deployment of medical imaging platforms, making advanced visualization accessible even in resource-limited settings.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see further convergence of AI, XR, and cloud technologies, with a focus on real-time, multi-user collaboration and integration with robotic surgery systems. Regulatory bodies are also working to standardize data formats and interoperability, which will accelerate adoption. As these innovations mature, volumetric medical data visualization is poised to become a cornerstone of precision medicine, enabling more personalized and effective care.
Leading Companies and Solutions: Profiles and Strategic Initiatives
The landscape of volumetric medical data visualization in 2025 is shaped by a cohort of leading technology companies, medical imaging specialists, and device manufacturers, each advancing the field through innovative solutions and strategic partnerships. These organizations are responding to the growing demand for high-fidelity, real-time visualization of complex medical datasets, driven by the proliferation of advanced imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, and PET.
Among the most prominent players is Siemens Healthineers, whose syngo.via platform integrates AI-powered volumetric rendering and multi-modality image fusion, supporting radiologists and clinicians in diagnostics and surgical planning. The company continues to invest in cloud-based collaboration tools and automated workflow enhancements, aiming to streamline the interpretation of large 3D datasets across distributed care teams.
GE HealthCare remains a key innovator, with its AW Advanced Visualization platform offering advanced 3D and 4D visualization, including cinematic rendering and quantitative analysis. In 2025, GE HealthCare is expanding its ecosystem through open APIs, enabling third-party developers and hospital IT teams to integrate custom AI algorithms and visualization modules, thus fostering a more flexible and interoperable environment.
Philips continues to push the boundaries with its IntelliSpace Portal, which leverages deep learning for automated segmentation and real-time volumetric rendering. The company’s strategic focus includes enhancing remote collaboration capabilities and integrating augmented reality (AR) for preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance, reflecting a broader industry trend toward immersive visualization.
In the software domain, Zebra Medical Vision and TeraRecon are notable for their AI-driven platforms that automate volumetric analysis and visualization. TeraRecon, in particular, is recognized for its Intuition platform, which supports advanced 3D/4D rendering and is increasingly being adopted in teleradiology and cloud-based diagnostic workflows.
Emerging players such as Medicalholodeck are pioneering the use of virtual reality (VR) for collaborative review of volumetric medical data, targeting both clinical and educational applications. Their solutions enable multiple users to interact with 3D datasets in immersive environments, a capability that is gaining traction as healthcare institutions seek new ways to enhance training and multidisciplinary case discussions.
Looking ahead, the sector is expected to see further convergence between AI, cloud computing, and immersive technologies, with leading companies investing in open platforms, interoperability, and real-time collaboration. Strategic initiatives are increasingly focused on reducing time-to-diagnosis, improving surgical outcomes, and democratizing access to advanced visualization tools across global healthcare systems.
Clinical Applications: From Radiology to Surgery and Beyond
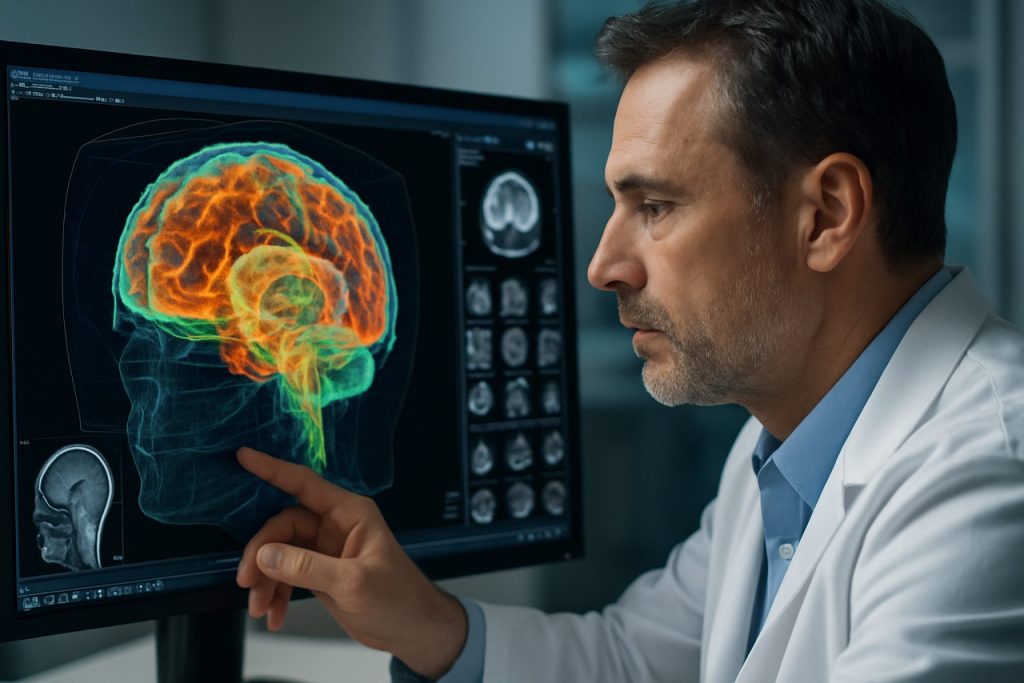
Volumetric medical data visualization is rapidly transforming clinical workflows across a spectrum of specialties, with 2025 marking a pivotal year for its integration into routine practice. The ability to render and interact with three-dimensional (3D) datasets—derived from modalities such as CT, MRI, and ultrasound—has become central to diagnostic radiology, surgical planning, and interventional procedures.
In radiology, volumetric visualization is now standard in advanced imaging suites, enabling radiologists to interpret complex anatomical relationships with greater accuracy. Leading imaging equipment manufacturers such as Siemens Healthineers, GE HealthCare, and Canon Medical Systems have integrated real-time 3D rendering engines into their latest scanners and workstations. These platforms support multi-planar reconstructions, maximum intensity projections, and cinematic rendering, which are particularly valuable in oncology, neurology, and cardiovascular imaging.
Surgical applications are seeing even more dramatic advances. Surgeons increasingly rely on volumetric visualization for preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation. Companies like Stryker and Medtronic are deploying visualization solutions that fuse patient-specific 3D data with augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) headsets, allowing surgeons to visualize anatomy overlaid on the patient during procedures. This is especially impactful in neurosurgery, orthopedics, and minimally invasive interventions, where precision is paramount.
Beyond radiology and surgery, volumetric visualization is expanding into pathology, cardiology, and even patient engagement. Digital pathology platforms are beginning to incorporate 3D reconstructions of tissue samples, while cardiology teams use volumetric echo and CT data to plan complex interventions such as transcatheter valve replacements. Patient-facing applications, such as those developed by Philips, are leveraging interactive 3D models to improve patient understanding and consent.
Looking ahead, the next few years will see further convergence of volumetric visualization with artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud-based collaboration. AI-driven segmentation and annotation tools are being embedded into visualization platforms, automating time-consuming tasks and enabling more personalized care. Cloud-native solutions from major vendors are facilitating remote multidisciplinary team meetings, where clinicians can collaboratively review and manipulate 3D datasets in real time.
As regulatory frameworks and interoperability standards mature, volumetric visualization is poised to become a ubiquitous tool across the clinical spectrum, driving improvements in diagnostic confidence, surgical outcomes, and patient engagement through 2025 and beyond.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with volumetric medical data visualization is rapidly transforming diagnostic workflows in 2025, with significant implications for accuracy, efficiency, and clinical outcomes. Volumetric data—such as that generated by CT, MRI, and PET scans—presents unique challenges due to its complexity and size. AI and ML algorithms are increasingly being embedded into visualization platforms to automate segmentation, highlight anomalies, and assist in pattern recognition, thereby reducing the cognitive load on radiologists and clinicians.
Leading medical imaging companies are at the forefront of this integration. Siemens Healthineers has incorporated AI-powered tools into its syngo.via platform, enabling automated organ segmentation and lesion detection in 3D datasets. These features not only accelerate the diagnostic process but also help standardize interpretations across practitioners. Similarly, GE HealthCare has advanced its Edison platform with deep learning models that enhance volumetric visualization, supporting clinicians in identifying subtle pathologies that may be missed by the human eye alone.
Another key player, Philips, has integrated AI-driven analytics into its IntelliSpace Portal, offering tools for automated quantification and visualization of complex anatomical structures. These solutions are designed to work seamlessly with large-scale 3D and 4D imaging data, providing clinicians with actionable insights in real time. Canon Medical Systems is also leveraging AI for advanced visualization, focusing on workflow automation and improved diagnostic confidence through its suite of imaging solutions.
The outlook for the next few years points to even deeper integration of AI and ML in volumetric visualization. Ongoing developments include the use of generative AI models to synthesize missing or low-quality data, as well as federated learning approaches that enable collaborative model training across institutions without compromising patient privacy. Industry leaders are also exploring explainable AI techniques to ensure that automated findings are transparent and interpretable by clinicians, addressing regulatory and ethical considerations.
As regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continue to approve AI-enabled imaging tools, adoption is expected to accelerate. The convergence of AI, ML, and volumetric visualization is poised to redefine diagnostic accuracy, reduce variability, and ultimately improve patient outcomes in the coming years.
Regulatory Landscape and Standards: Compliance and Interoperability
The regulatory landscape for volumetric medical data visualization is rapidly evolving in 2025, reflecting the increasing integration of advanced imaging technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) into clinical workflows. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and international standards organizations are intensifying their focus on compliance, safety, and interoperability for software handling 3D and 4D medical imaging data.
A central regulatory requirement is adherence to the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard, which ensures interoperability between imaging devices, visualization software, and healthcare information systems. The DICOM standard, maintained by the Medical Imaging & Technology Alliance, continues to expand its specifications to accommodate new modalities and volumetric data types, including multi-frame and time-resolved datasets. In 2025, updates to DICOM are increasingly addressing AI-generated segmentations and annotations, supporting seamless integration of advanced visualization tools into radiology and surgical planning workflows.
The FDA’s Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) framework remains a cornerstone for regulatory compliance in the United States. Visualization platforms that process, render, or analyze volumetric data—such as those developed by Siemens Healthineers, GE HealthCare, and Philips—must demonstrate robust validation, cybersecurity, and risk management processes. In 2025, the FDA is placing greater emphasis on real-world performance monitoring and post-market surveillance, especially for AI-powered visualization tools that adapt over time.
In Europe, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) are fully in force, requiring comprehensive clinical evaluation and conformity assessment for software-based medical devices. Companies must provide evidence of interoperability, data integrity, and patient safety, with a particular focus on the traceability of volumetric data transformations and outputs. Leading vendors are increasingly collaborating with standards bodies and regulatory agencies to ensure their platforms—such as Siemens Healthineers’ syngo.via and GE HealthCare’s AW Server—meet these stringent requirements.
Looking ahead, the regulatory outlook for volumetric medical data visualization is expected to further emphasize interoperability, transparency, and explainability, particularly as AI-driven tools become more prevalent. Initiatives such as Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE), supported by the Radiological Society of North America, are driving the adoption of standardized workflows and data exchange protocols. As healthcare systems worldwide accelerate digital transformation, compliance with evolving standards and regulations will remain a critical factor for technology providers and healthcare organizations alike.
Challenges and Barriers: Data Management, Security, and Adoption
Volumetric medical data visualization, which enables clinicians to interpret complex 3D datasets from modalities such as CT, MRI, and PET, is rapidly advancing. However, as of 2025, several significant challenges and barriers persist in the areas of data management, security, and adoption.
Data Management: The sheer volume and complexity of medical imaging data present ongoing hurdles. Modern scanners generate high-resolution, multi-gigabyte datasets per patient, straining storage infrastructure and network bandwidth. Efficient data compression, lossless archiving, and rapid retrieval remain critical needs. Leading imaging equipment manufacturers such as Siemens Healthineers and GE HealthCare are investing in advanced data management solutions, including cloud-based platforms and AI-driven data triage, to address these issues. However, interoperability between different vendor systems and legacy PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) continues to be a barrier, often requiring custom integration and data migration efforts.
Security: The sensitive nature of medical imaging data makes security paramount. Healthcare organizations face increasing threats from cyberattacks, including ransomware targeting imaging archives and visualization workstations. Regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe mandate strict controls over data access, transmission, and storage. Companies like Philips and Canon Medical Systems are enhancing their platforms with end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and audit trails. Despite these advances, the distributed nature of modern visualization—often involving remote access and cloud-based rendering—introduces new vulnerabilities, requiring continuous updates and staff training.
Adoption: While volumetric visualization offers clear clinical benefits, adoption is uneven across regions and institutions. High upfront costs for advanced workstations, software licenses, and training can be prohibitive, especially for smaller hospitals and clinics. Furthermore, workflow integration remains a challenge; radiologists and surgeons must adapt to new interfaces and visualization paradigms, which can slow clinical routines. Industry leaders such as Siemens Healthineers and GE HealthCare are addressing these barriers by offering scalable, subscription-based solutions and investing in user-friendly interfaces. Nevertheless, the need for standardized training and certification in volumetric visualization persists, as does the challenge of demonstrating clear return on investment to healthcare administrators.
Looking ahead, overcoming these challenges will require coordinated efforts among technology providers, healthcare institutions, and regulatory bodies. Advances in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and interoperability standards are expected to gradually reduce barriers, but widespread, seamless adoption of volumetric medical data visualization will likely remain a work in progress through the next several years.
Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Emerging Markets
The global landscape for volumetric medical data visualization is rapidly evolving, with distinct trends and growth drivers across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and emerging markets. As of 2025, the adoption of advanced visualization technologies is being shaped by regional healthcare infrastructure, regulatory environments, and investment in digital health.
North America remains at the forefront of volumetric medical data visualization, driven by robust healthcare systems, early adoption of digital imaging, and a strong presence of leading technology providers. Companies such as GE HealthCare, Siemens Healthineers, and Philips have established significant R&D and commercial operations in the United States and Canada, supporting the integration of 3D and 4D visualization into clinical workflows. The region benefits from a high concentration of academic medical centers and a favorable reimbursement environment for advanced imaging, which accelerates the deployment of volumetric visualization in radiology, oncology, and surgical planning.
Europe is characterized by strong regulatory oversight and a focus on interoperability and data privacy. The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) shape the development and deployment of visualization solutions. Major players such as Siemens Healthineers (headquartered in Germany) and Philips (Netherlands) are deeply involved in collaborative projects with hospitals and research institutes to advance volumetric imaging, particularly in precision medicine and minimally invasive interventions. The region is also seeing increased investment in AI-driven visualization tools, with a focus on cross-border data sharing and telemedicine.
Asia-Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth in volumetric medical data visualization, propelled by expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising demand for advanced diagnostics, and government initiatives to modernize medical imaging. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing heavily in digital health, with local and multinational companies establishing partnerships to deploy 3D visualization platforms. Canon Medical Systems (Japan) and Samsung Medison (South Korea) are notable regional players, contributing to the proliferation of volumetric imaging in both urban and rural healthcare settings.
Emerging markets in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are gradually adopting volumetric visualization technologies, albeit at a slower pace due to budget constraints and limited access to high-end imaging equipment. However, international collaborations and mobile health initiatives are beginning to bridge the gap. Companies like GE HealthCare and Philips are expanding their presence through affordable solutions and training programs, aiming to increase the accessibility of volumetric imaging in underserved regions.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see continued regional convergence, with North America and Europe driving innovation, Asia-Pacific leading in adoption rates, and emerging markets gradually increasing their uptake through targeted investments and technology transfer.
Future Outlook: Next-Generation Visualization and Market Opportunities
The future of volumetric medical data visualization is poised for significant transformation as healthcare providers, technology developers, and device manufacturers accelerate innovation in response to growing clinical demands and technological advancements. By 2025 and in the following years, the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and advanced display technologies is expected to redefine how volumetric data—such as CT, MRI, and ultrasound scans—are interpreted and utilized in clinical practice.
Key industry players are investing heavily in next-generation visualization platforms. Siemens Healthineers continues to expand its AI-powered imaging solutions, integrating deep learning algorithms to enhance 3D and 4D image reconstruction, segmentation, and real-time analysis. Similarly, GE HealthCare is advancing its Edison platform, which leverages cloud-based analytics and visualization tools to facilitate collaborative diagnostics and remote consultations. These platforms are designed to handle increasingly large and complex datasets, supporting precision medicine and personalized treatment planning.
The adoption of extended reality (XR) technologies—including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR)—is accelerating, with companies like Philips and Canon Medical Systems developing immersive visualization solutions for surgical planning, education, and intraoperative guidance. These systems enable clinicians to interact with volumetric data in three dimensions, improving spatial understanding and potentially reducing procedural risks. The integration of haptic feedback and gesture-based controls is anticipated to further enhance user experience and clinical utility.
Cloud-native platforms are also gaining traction, enabling secure, scalable access to volumetric imaging data across institutions and geographies. Intuitive Surgical, known for its robotic-assisted surgery systems, is exploring cloud-based visualization to support remote proctoring and tele-mentoring, while Stryker is investing in interoperable solutions that connect imaging, navigation, and surgical devices in real time.
Looking ahead, the market for volumetric medical data visualization is expected to benefit from regulatory support for digital health innovation and increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures. The next few years will likely see broader adoption of AI-driven automation, real-time 3D rendering, and cross-platform interoperability. As these technologies mature, they are set to unlock new opportunities in diagnostics, therapy planning, and patient engagement, positioning volumetric visualization as a cornerstone of next-generation healthcare delivery.
Sources & References
- Siemens Healthineers
- GE HealthCare
- Philips
- Microsoft
- Canonical
- TeraRecon
- Medicalholodeck
- Medtronic
- Medical Imaging & Technology Alliance
- Radiological Society of North America
- Canon Medical Systems
- Intuitive Surgical