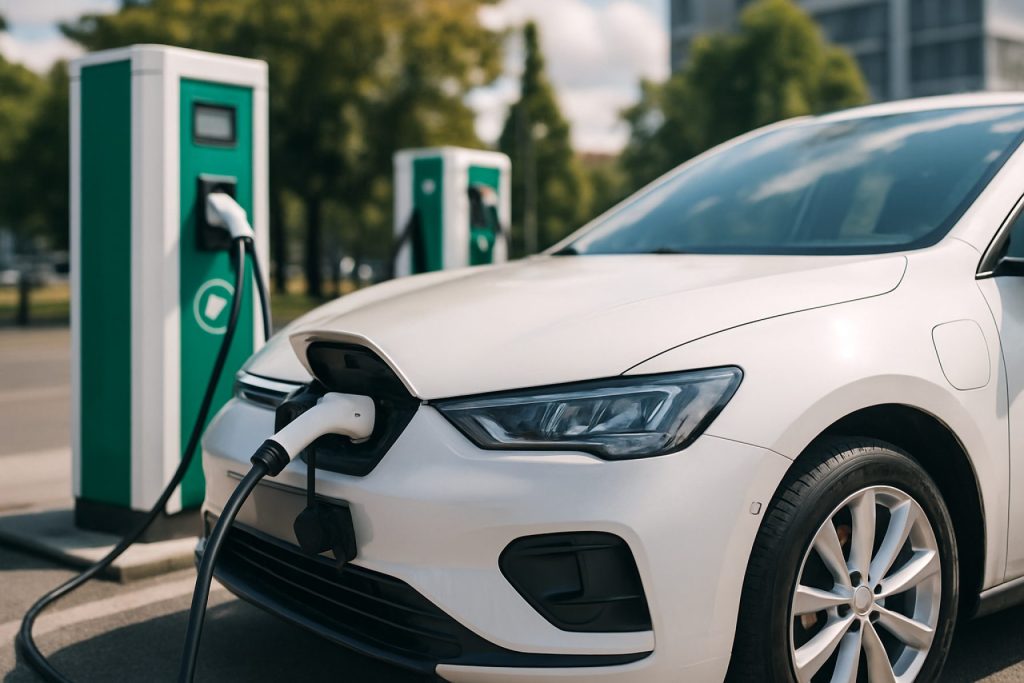
- The electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure market is growing rapidly, with projected annual growth over 36% through 2032.
- Europe leads in EV adoption and charging networks, driven by strict emission goals and heavy investment.
- North America is accelerating expansion, with government support and major contributions from companies like Tesla and ChargePoint.
- DC fast charging technology enables rapid recharging, while home charging with Level II chargers remains most common.
- Key challenges include high installation costs, grid capacity issues, inconsistent standards, and maintenance concerns.
- Innovations such as renewable-powered stations, smart technology, and vehicle-to-grid integration aim to strengthen the EV ecosystem.
- Success will depend on adaptability, investment, and seamless user experiences as global electrification races ahead.
Every urban skyline now shadows the future—sleek charging stations stand shoulder to shoulder with gas pumps, humming quietly as they power up zero-emission machines. The world’s shift to electric vehicles (EVs) has set the stage for a monumental expansion in charging infrastructure, outpacing even the wildest hopes of early clean-energy advocates.
Charged Ambitions and a Race Against Time
A global race is underway: by 2032, the electric vehicle charging station market is projected to balloon at an astonishing annual growth rate above 36%. Cities and highways around the world are under transformation. Planners and private innovators scramble to install fast-charging points where they’re needed most—urban centers, bustling highways, sleepy residential neighborhoods.
Europe leads the charge, fueled by aggressive emission targets and investments topping billions of euros. Take Norway, where over 80% of new car sales are fully electric, or Germany and the Netherlands, whose web of DC fast chargers enable drivers to crisscross nations with confidence. In these lands, fossil fuels are fading into the rearview mirror.
North America, always a land of reinvention, is catching up. Large-scale federal infrastructure initiatives—and players like Tesla—are reshaping the EV landscape. Tesla’s announcement to open its vaunted Supercharger network to non-Tesla EVs across Europe signals a seismic shift toward interoperability and convenience. Meanwhile, American companies such as ChargePoint and General Electric pour resources into variety, reliability, and expansion.
Technology at the Center
Step into a modern charging station and you’ll see a story of relentless innovation. Fast-charging DC units, using standards like CHAdeMO and CCS, can electrify a depleted battery in less time than it takes to finish a cup of coffee. These high-voltage marvels are critical for busy drivers and commercial fleets, slashing vehicle downtime.
Yet, most drivers still favor the tranquility of charging at home, often overnight, with affordable Level II chargers. Residential installations dominate, but public infrastructure is booming—urgent and ubiquitous as cities rethink what “fueling up” means in this new era.
Opportunities and Growing Pains
Under this gleaming surface, challenges ripple. High installation costs for fast chargers, grid congestion, and patchy standards threaten to stall momentum, particularly in emerging markets. Even in developed regions, maintenance woes and vandalism sometimes disrupt the smooth promise of electrified mobility.
But necessity breeds innovation. Governments press ahead with subsidies and public-private partnerships. Companies experiment with solar- and wind-powered stations, integrating smart tech and payment systems to make EV charging as frictionless as possible. The horizon stretches further still: a world in which cars feed energy back into the grid during peak demand, through vehicle-to-grid solutions, turning vehicles into rolling power plants.
The Takeaway
One truth charges through all the headlines: the electrification of transport is not a distant vision—it’s happening now, all around us. The winners in this unfolding saga will be those who adapt quickly, break barriers, and turn the everyday necessity of refueling into an act as effortless—and sustainable—as flipping a light switch. As the market swells and the world’s energy habits change, one question remains for communities, companies, and drivers: Who will keep pace with the charge?
The Shocking Rise of EV Charging: Hidden Realities, Life Hacks, and Market Moves You Need to Know
# The Rapid Evolution of EV Charging Infrastructure: Beyond the Headlines
The global shift to electric vehicles (EVs) is turbocharging a revolution in how the world thinks about mobility, sustainability, and even personal convenience. While city skylines and highways transform, intriguing aspects of the EV charging ecosystem are often overshadowed by eye-popping growth projections. Let’s dig deeper, answering critical questions, providing real-world strategies, and making sense of what’s next for consumers, companies, and city planners.
—
Key Market Stats and Industry Trends
– Exponential Market Growth: By 2032, the global EV charging station market is forecast to surpass $154 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36%+ ([source](https://www.bloomberg.com/)). Home, workplace, and public chargers are collectively fueling this staggering pace.
– Shift Toward Ultra-Fast Charging: Major manufacturers like ABB and Tesla are betting big on 350 kW and higher chargers, slashing recharge times to 10–15 minutes for compatible vehicles.
– Emerging Market Dynamics: China leads in charging point installations—over 1.8 million as of 2023—thanks to government mandates and incentives (International Energy Agency).
– North American Expansion: The U.S. is investing $7.5 billion as part of its national infrastructure plan, aiming for half a million chargers by 2030 ([U.S. Department of Energy](https://www.energy.gov/)).
—
Specs, Pricing, and Technological Innovations
Types of Chargers
| Charger Level | Voltage | Charge Time (to 80%) | Locations | Estimated Cost per Unit |
|——————-|———|———————-|——————————|—————————–|
| Level 1 | 120V | 24–40 hours | Homes, public places | $200–$600 |
| Level 2 | 208–240V| 4–10 hours | Homes, workplaces, retail | $500–$2,000 |
| DC Fast Charger | 400V+ | 15–60 minutes | Highways, commercial hubs | $15,000–$50,000+ |
Does not include installation costs, which can be $1,000–$10,000 depending on electrical upgrades.
Key Features and Compatibility
– Standards: CCS (Combined Charging System) dominates in Europe and North America; CHAdeMO remains popular in Japan.
– Smart Charging: Many modern chargers are connected to apps, enabling remote monitoring, scheduling, and even dynamic electricity pricing.
– Payment Systems: Expect RFID, mobile app integration, and even credit card tap-to-pay options becoming standard.
—
How-To Guide: Finding and Using EV Chargers
1. Find Reliable Stations: Use trusted apps like PlugShare or manufacturer apps from ChargePoint and Tesla.
2. Plan Charging Stops: For road trips, map fast-charger networks along your route; don’t rely solely on car navigation.
3. Understand Your Adapter: Make sure your EV supports local standards (CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla).
4. Check Real-Time Availability: Crowdsourced and network-updated data helps avoid station downtime.
5. Optimize Home Charging: Install a Level 2 charger with smart scheduling to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
6. Register for Multiple Networks: Enhance charging flexibility for cross-country trips.
—
Pros & Cons Overview
Pros
– Convenience: Overnight home charging means a “full tank” each morning.
– Lower Operating Costs: Electricity is often much cheaper than gasoline.
– Environmental Impact: Zero tailpipe emissions.
– Grid Benefits: Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology can help stabilize local power supply.
Cons
– Upfront Costs: Chargers, installation, and home electrical upgrades can be costly.
– Uneven Access: Urban and rural discrepancies in charger availability.
– Wait Times: Limited fast-charger throughput during high-demand periods.
– Interoperability: Not all stations support all car types—adapters may be needed.
—
Controversies and Limitations
– Grid Strain: Mass adoption could overload local substations if upgrades lag.
– Vandalism & Maintenance: Public chargers are sometimes targeted, causing unexpected outages.
– Battery Degradation: Frequent use of fast charging may marginally accelerate battery wear (U.S. Department of Energy).
—
Security & Sustainability Insights
– Data Privacy Risks: Smart chargers collect usage data; ensure your provider adheres to regional privacy laws and cybersecurity standards.
– Green Energy Integration: Companies are piloting solar- and wind-powered EV stations, further cutting carbon footprints.
—
Reviews & Brand Comparisons
– Tesla Supercharger vs. ChargePoint vs. Electrify America
– Tesla: Fastest, most reliable (for Tesla cars), expanding universal compatibility.
– ChargePoint: Broadest network, excellent home charger options, seamless app.
– Electrify America: Rapidly growing highway network, focus on non-Tesla vehicles, accepts multiple payment types.
—
Pressing Questions Answered
Q: Will more chargers mean the end of “range anxiety”?
– A: Network density is improving rapidly, but rural and remote areas still need attention. Planning remains key for long trips.
Q: How soon will charging be as fast as gasoline fueling?
– A: Ultra-fast charging (under 10 minutes) is here for select high-end EVs, but broad rollout depends on grid upgrades and vehicle compatibility.
Q: Is it safe to charge an EV in the rain or snow?
– A: Yes—chargers are designed to operate safely in inclement weather. Always use certified equipment.
—
Actionable Quick Tips
– Plan Charging Ahead: Always plot your next charge before your battery drops below 20%, especially outside major cities.
– Install Smart Home Chargers: Take advantage of local rebates and tax credits—many regions subsidize installation costs.
– Monitor Incentives: Stay updated on federal, state, and municipal programs for new installations and EV purchases ([U.S. Department of Energy](https://www.energy.gov/)).
—
Forecast & Predictions
– Fleet Electrification: Delivery, rideshare, and public transport fleets will set new benchmarks for rapid DC charger deployment.
– Urban Innovation: Expect more “charging hubs” at retail plazas, public parking, and curbside locations over the next 3–5 years.
– Resale Value Boost: Homes with dedicated EV charging can command higher prices as adoption grows (National Association of Realtors).
—
Final Thoughts
The electrification revolution is here—and those who adapt now will reap the rewards in cost, convenience, and sustainability. Start by exploring reputable charger networks such as ChargePoint, or stay informed on breakthroughs from industry leaders like General Electric and Tesla. Smart charging is more than just a tech upgrade—it’s the new normal.
Stay plugged in, stay prepared, and ride the current into a cleaner, more electrified future!