How Augmented Reality Surgical Guidance Systems Are Transforming Operating Rooms in 2025: A Deep Dive into Market Acceleration, Breakthrough Technologies, and the Future of Surgical Precision
- Executive Summary: 2025 Market Landscape and Key Takeaways
- Market Size, Growth Rate, and Forecasts Through 2030
- Core Technologies Powering AR Surgical Guidance Systems
- Leading Companies and Recent Innovations (e.g., medtronic.com, siemens-healthineers.com, philips.com)
- Clinical Applications: From Neurosurgery to Orthopedics
- Integration with Robotics, Imaging, and AI
- Regulatory Environment and Industry Standards (e.g., fda.gov, ieee.org)
- Adoption Barriers and Enablers: Training, Cost, and Workflow
- Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Emerging Markets
- Future Outlook: Next-Gen AR, Market Opportunities, and Strategic Recommendations
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: 2025 Market Landscape and Key Takeaways
The market for Augmented Reality (AR) Surgical Guidance Systems is entering a pivotal phase in 2025, marked by accelerated clinical adoption, robust investment, and expanding regulatory clearances. AR technologies are increasingly being integrated into operating rooms to enhance visualization, precision, and workflow efficiency across a range of surgical specialties, including orthopedics, neurosurgery, and minimally invasive procedures.
Key industry leaders such as Medtronic, Smith+Nephew, and Stryker are actively advancing AR-enabled platforms. For example, Medtronic’s StealthStation™ system and Stryker’s AR-based guidance solutions are being deployed in major hospitals, supporting complex spinal and cranial surgeries. Smith+Nephew’s ARIA platform is also gaining traction for its application in orthopedic navigation and planning. These systems leverage real-time data overlays, 3D anatomical mapping, and intraoperative imaging to improve surgical accuracy and reduce complication rates.
In 2025, the market is characterized by a surge in partnerships between device manufacturers and software innovators. Companies such as Brainlab and Augmedics are notable for their AR navigation solutions, with Brainlab’s Mixed Reality Viewer and Augmedics’ xvision Spine System receiving expanded regulatory approvals in North America and Europe. These developments are enabling broader clinical trials and real-world evidence generation, which are critical for further reimbursement and adoption.
The competitive landscape is also shaped by the entry of technology giants and specialized startups. Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 is being integrated into surgical workflows through collaborations with medical device firms, while startups like SentiAR are introducing advanced visualization tools for interventional procedures. The convergence of AR with artificial intelligence and robotics is anticipated to drive the next wave of innovation, with several pilot programs underway in leading academic medical centers.
Looking ahead, the outlook for AR surgical guidance systems is highly favorable. The sector is expected to benefit from ongoing improvements in hardware ergonomics, software interoperability, and cloud-based data management. Regulatory agencies are increasingly providing clear pathways for AR device approvals, and early health economic data suggest potential reductions in operative time and improved patient outcomes. As a result, AR surgical guidance is poised to transition from early adoption to standard of care in select procedures over the next few years, with global expansion anticipated as infrastructure and training programs mature.
Market Size, Growth Rate, and Forecasts Through 2030
The global market for Augmented Reality (AR) Surgical Guidance Systems is experiencing robust growth, driven by technological advancements, increased adoption in operating rooms, and expanding clinical validation. As of 2025, the market is estimated to be valued in the low single-digit billions (USD), with North America and Europe leading in adoption, followed by rapid uptake in Asia-Pacific. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for this sector is projected to remain in the high teens through 2030, reflecting both the increasing number of AR-assisted procedures and the broadening range of surgical specialties integrating these systems.
Key players in the AR surgical guidance space include Medtronic, which offers the StealthStation platform integrating AR for neurosurgical navigation, and Smith+Nephew, whose AR-enabled surgical guidance solutions are being adopted in orthopedics and sports medicine. Stryker has also expanded its AR portfolio, particularly in spine and joint replacement surgeries, while Brainlab continues to innovate with its Mixed Reality Viewer and Elements software suite, supporting a range of cranial and spinal procedures.
Recent years have seen a surge in clinical trials and hospital deployments, with AR systems demonstrating improved surgical accuracy, reduced operative times, and enhanced training capabilities. For example, Medtronic reported increased utilization of its AR navigation systems in minimally invasive spine surgeries, while Brainlab has documented over 1,000 installations of its AR-enabled platforms worldwide. The integration of AR with robotic-assisted surgery and artificial intelligence is expected to further accelerate market growth, as these technologies converge to offer real-time, data-rich guidance for complex procedures.
Looking ahead to 2030, the AR surgical guidance market is forecast to surpass $5 billion globally, with procedure volumes and system installations expanding rapidly in both developed and emerging markets. Growth will be fueled by ongoing improvements in AR hardware (such as lighter, wireless headsets), broader regulatory approvals, and increasing evidence of clinical and economic benefits. Strategic partnerships between device manufacturers, software developers, and healthcare providers are anticipated to drive innovation and adoption, positioning AR surgical guidance as a standard of care in multiple surgical disciplines.
Core Technologies Powering AR Surgical Guidance Systems
Augmented Reality (AR) surgical guidance systems are rapidly transforming the landscape of operative medicine, leveraging a suite of advanced core technologies to enhance precision, safety, and efficiency in the operating room. As of 2025, the integration of real-time imaging, computer vision, spatial mapping, and wearable hardware is central to the evolution and adoption of these systems.
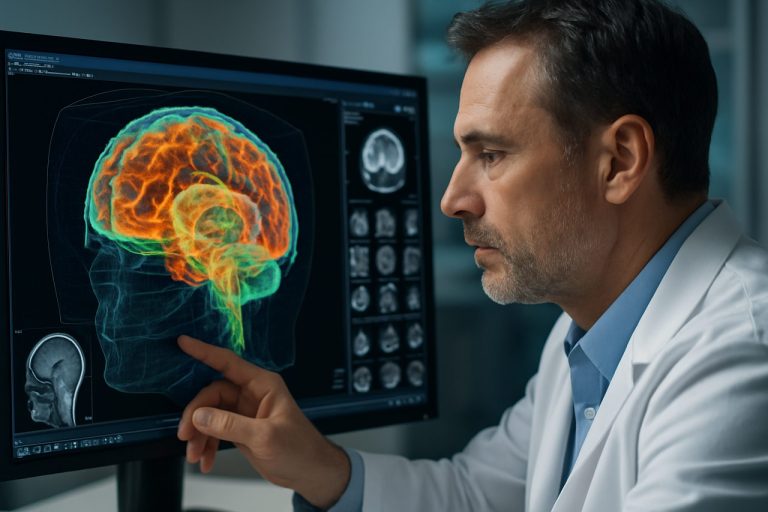
At the heart of AR surgical guidance is the fusion of intraoperative imaging modalities—such as CT, MRI, and fluoroscopy—with real-time data processing. This enables the overlay of critical anatomical information directly onto the surgeon’s field of view. Companies like Siemens Healthineers and GE HealthCare are at the forefront, providing high-resolution imaging platforms that seamlessly integrate with AR software, allowing for dynamic visualization of patient anatomy during procedures.
Computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are pivotal in interpreting imaging data and tracking surgical instruments with sub-millimeter accuracy. These technologies facilitate the registration and alignment of virtual overlays with the patient’s actual anatomy, even as tissues shift during surgery. Medtronic has advanced this field with its StealthStation platform, which combines optical tracking and AI-driven navigation to support neurosurgical and spinal procedures.
Spatial mapping and depth sensing are equally critical, enabling AR systems to construct accurate 3D models of the surgical environment. Devices such as the Microsoft HoloLens 2, used by partners like Philips in their augmented reality solutions, employ advanced sensors and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms to maintain precise spatial awareness. This ensures that digital overlays remain stable and correctly positioned relative to the patient, even as the surgeon moves.
Wearable AR hardware, including head-mounted displays (HMDs) and smart glasses, is becoming increasingly ergonomic and robust. Companies such as Augmedics have developed FDA-cleared systems like xvision, which project 3D anatomical data directly into the surgeon’s line of sight, eliminating the need to look away from the operative field. These devices are designed for sterility, comfort, and extended use, addressing key barriers to clinical adoption.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to bring further miniaturization of hardware, improved wireless connectivity, and deeper integration with hospital information systems. Open platforms and interoperability standards are also emerging, led by industry collaborations and organizations such as Intuitive Surgical, to ensure seamless data exchange and workflow optimization. As these core technologies mature, AR surgical guidance systems are poised to become standard tools across a growing range of surgical specialties.
Leading Companies and Recent Innovations (e.g., medtronic.com, siemens-healthineers.com, philips.com)
The landscape of augmented reality (AR) surgical guidance systems is rapidly evolving, with several leading medical technology companies driving innovation and adoption in 2025. These systems integrate real-time imaging, advanced visualization, and precise navigation to enhance surgical accuracy and outcomes. The following section highlights key players and their recent advancements in this sector.
- Medtronic has emerged as a frontrunner in AR-assisted surgery, building on its established expertise in surgical navigation. The company’s StealthStation platform, which integrates AR overlays with intraoperative imaging, continues to see expanded clinical use, particularly in neurosurgery and spine procedures. In 2024 and 2025, Medtronic has focused on refining its AR visualization capabilities, enabling surgeons to superimpose 3D anatomical models directly onto the operative field, thereby improving precision and reducing operative times. The company is also investing in AI-driven enhancements to further personalize surgical planning and intraoperative guidance (Medtronic).
- Siemens Healthineers has advanced its AR offerings through the integration of its ARTIS icono angiography system with AR navigation tools. In 2025, Siemens Healthineers is piloting next-generation AR modules that allow for real-time fusion of preoperative imaging with live fluoroscopy, supporting complex cardiovascular and interventional radiology procedures. The company’s focus on seamless workflow integration and interoperability with hospital IT systems is positioning its AR solutions for broader adoption in hybrid operating rooms (Siemens Healthineers).
- Philips continues to expand its augmented reality portfolio, leveraging its Azurion image-guided therapy platform. In 2025, Philips is rolling out enhanced AR applications that provide surgeons with holographic overlays of patient anatomy, accessible via head-mounted displays or integrated monitors. These innovations are being deployed in minimally invasive cardiac and vascular interventions, with early clinical data indicating improved navigation accuracy and reduced radiation exposure for both patients and staff (Philips).
- Brainlab, a specialist in digital surgery and medical software, has made significant strides with its Mixed Reality Viewer and Elements software suite. In 2025, Brainlab is collaborating with major academic hospitals to validate the clinical impact of AR-guided tumor resections and orthopedic procedures. The company’s open platform approach allows integration with third-party imaging and navigation systems, fostering a growing ecosystem of AR-enabled surgical tools (Brainlab).
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to see accelerated adoption of AR surgical guidance systems, driven by ongoing improvements in hardware (such as lighter, higher-resolution headsets), AI-powered image processing, and greater interoperability across surgical platforms. As regulatory approvals expand and clinical evidence accumulates, AR is poised to become a standard adjunct in complex surgical procedures, with leading companies at the forefront of this transformation.
Clinical Applications: From Neurosurgery to Orthopedics
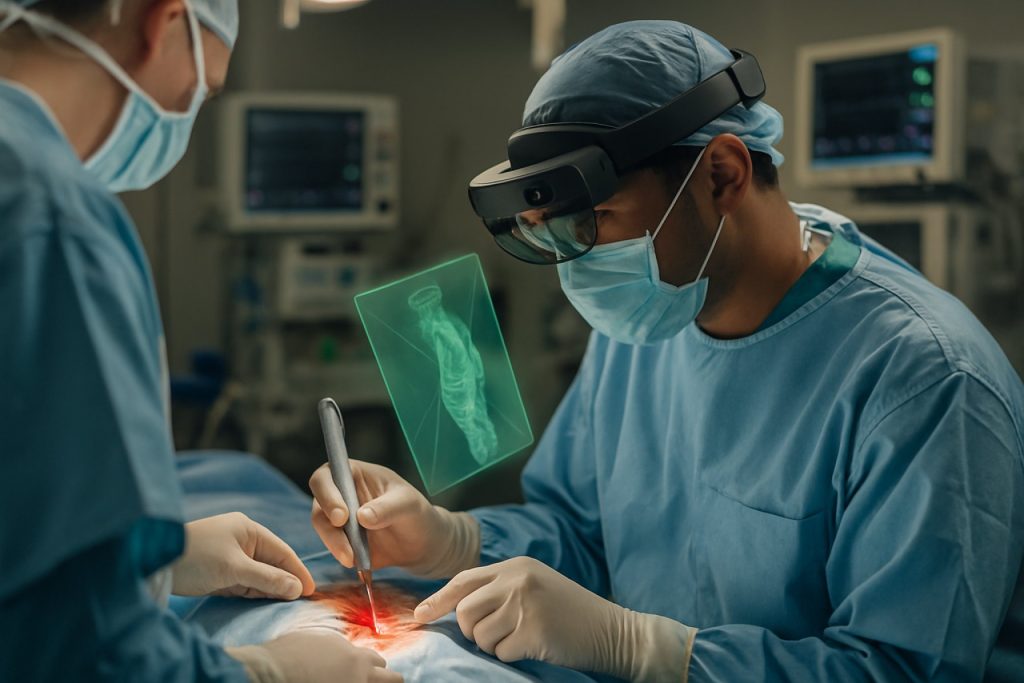
Augmented Reality (AR) surgical guidance systems are rapidly transforming clinical practice across multiple specialties, with neurosurgery and orthopedics at the forefront of adoption in 2025. These systems overlay digital information—such as anatomical structures, surgical plans, and instrument trajectories—directly onto the surgeon’s field of view, enhancing precision and intraoperative decision-making.
In neurosurgery, AR platforms are being integrated with preoperative imaging and navigation systems to improve tumor resections, vascular interventions, and spinal procedures. For example, Brainlab AG has advanced its Mixed Reality Viewer and Elements software suite, enabling surgeons to visualize 3D patient data in real time during cranial and spinal operations. These tools are now being used in leading academic centers, with early clinical studies reporting improved accuracy in tumor localization and reduced operative times.
Orthopedic surgery is another area witnessing significant AR adoption. Smith+Nephew has commercialized its AR-based surgical guidance platform, the Real Intelligence suite, which includes the CORI Surgical System. This system assists surgeons in knee and hip arthroplasty by projecting real-time alignment and resection data, aiming to improve implant positioning and patient outcomes. Similarly, Medacta International has introduced AR-enhanced navigation for joint replacement, with early clinical feedback indicating increased procedural confidence and workflow efficiency.
Spine surgery is also benefiting from AR guidance. Augmedics has developed the xvision Spine System, an FDA-cleared headset that superimposes navigation data onto the surgeon’s view, allowing for “see-through” visualization of vertebrae and instruments. As of 2025, this technology is being adopted in both the United States and Europe, with published case series demonstrating high pedicle screw placement accuracy and reduced radiation exposure compared to traditional fluoroscopy.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to bring broader clinical validation and integration of AR systems across additional surgical domains, including ENT, maxillofacial, and trauma surgery. Ongoing collaborations between device manufacturers and hospital networks are focused on generating large-scale outcome data and refining user interfaces for seamless operating room integration. As AR hardware becomes lighter and more ergonomic, and as software platforms achieve greater interoperability with hospital IT systems, the clinical impact of AR surgical guidance is poised to expand significantly, supporting safer, more efficient, and more personalized surgical care.
Integration with Robotics, Imaging, and AI
The integration of augmented reality (AR) surgical guidance systems with robotics, advanced imaging, and artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of operative medicine in 2025. This convergence is driven by the need for greater precision, efficiency, and safety in complex surgical procedures. AR overlays digital information onto the surgeon’s field of view, while robotics and AI provide enhanced dexterity, automation, and data-driven insights.
Robotic-assisted surgery platforms are increasingly incorporating AR modules to improve intraoperative navigation. For example, Intuitive Surgical, the manufacturer of the da Vinci robotic system, has been developing AR-enhanced visualization tools that allow surgeons to superimpose 3D anatomical models onto the operative field. This integration enables more accurate targeting and manipulation of tissues, particularly in minimally invasive procedures. Similarly, Medtronic has advanced its Mazor X Stealth Edition robotic guidance system by combining real-time imaging, AR overlays, and AI-driven analytics to optimize spinal surgery workflows.
Imaging technologies are also central to the evolution of AR surgical guidance. Intraoperative CT, MRI, and fluoroscopy are being fused with AR platforms to provide real-time, context-aware guidance. Siemens Healthineers and GE HealthCare are actively developing solutions that integrate their advanced imaging modalities with AR navigation, allowing surgeons to visualize subsurface structures and critical anatomy with unprecedented clarity. These systems are designed to reduce the risk of complications and improve surgical outcomes by providing continuous, dynamic feedback during procedures.
- AI algorithms are increasingly embedded within AR surgical guidance systems to assist with image segmentation, anatomical landmark identification, and intraoperative decision support. Companies like Stryker are leveraging AI to automate the registration of patient-specific data and enhance the accuracy of AR overlays, particularly in orthopedics and neurosurgery.
- The next few years are expected to see further convergence, with AR platforms becoming more interoperable with hospital information systems, robotic arms, and imaging devices. Open architecture and standardized data protocols are being prioritized to facilitate seamless integration and scalability.
- Regulatory approvals and clinical validation studies are accelerating, with several AR-robotics-imaging hybrid systems entering routine clinical use in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Looking ahead, the synergy between AR, robotics, imaging, and AI is poised to redefine surgical workflows, enabling more personalized, minimally invasive, and data-driven interventions. As these technologies mature, their adoption is expected to expand beyond tertiary centers to community hospitals and ambulatory surgical settings, democratizing access to advanced surgical care.
Regulatory Environment and Industry Standards (e.g., fda.gov, ieee.org)
The regulatory environment for Augmented Reality (AR) Surgical Guidance Systems is rapidly evolving as these technologies transition from experimental deployments to routine clinical use. In the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a central role in evaluating and approving AR-based medical devices. As of 2025, several AR surgical navigation platforms have received FDA 510(k) clearance, including systems from Medtronic and Smith+Nephew, reflecting growing regulatory confidence in the safety and efficacy of these solutions.
The FDA’s regulatory framework for AR surgical systems generally classifies them as Class II medical devices, requiring demonstration of substantial equivalence to predicate devices. However, the agency has signaled increased scrutiny for software-driven and AI-enabled features, emphasizing the need for robust clinical validation, cybersecurity safeguards, and transparent user interfaces. In 2024, the FDA issued updated guidance on “Clinical Decision Support Software,” which directly impacts AR platforms that provide intraoperative recommendations or overlays, clarifying the boundary between assistive visualization and active clinical decision-making.
Internationally, the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) has imposed stricter requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, affecting AR system manufacturers seeking CE marking. Companies such as Brainlab and Augmedics have adapted their regulatory strategies to comply with these evolving standards, investing in multicenter clinical trials and real-world evidence collection.
Industry standards are also maturing. The IEEE has established working groups focused on interoperability, data security, and user interface design for medical AR systems. The IEEE 11073 family of standards, traditionally used for medical device communication, is being extended to address the unique requirements of AR-enabled surgical guidance, such as real-time data integration and latency minimization. In parallel, the ASTM International is developing guidelines for the validation and performance assessment of AR visualization in surgical environments.
Looking ahead, regulatory agencies are expected to further refine their approaches as AR surgical guidance becomes more prevalent and complex, particularly with the integration of AI and cloud-based analytics. Stakeholders anticipate increased harmonization of standards across jurisdictions, facilitating global market access while ensuring patient safety and clinical effectiveness.
Adoption Barriers and Enablers: Training, Cost, and Workflow
The adoption of Augmented Reality (AR) surgical guidance systems is accelerating in 2025, yet several barriers and enablers continue to shape their integration into clinical practice. Key factors influencing uptake include training requirements, cost considerations, and workflow integration.
Training and Clinical Acceptance
A primary barrier remains the need for specialized training. AR systems, such as those developed by Medtronic and Smith+Nephew, require surgeons and operating room staff to adapt to new visualization interfaces and interaction paradigms. While these companies offer structured training modules and simulation environments, the learning curve can be significant, particularly for complex procedures. In 2025, leading academic hospitals are increasingly partnering with manufacturers to establish AR training centers, aiming to accelerate proficiency and clinical confidence.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Cost remains a substantial barrier, especially for smaller hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers. The initial investment for AR hardware—such as head-mounted displays and tracking systems—along with ongoing software licensing and maintenance, can be prohibitive. For example, Stryker and Augmedics have introduced tiered pricing models and leasing options to lower the entry threshold. Additionally, some health systems are exploring shared-use models, where AR systems are deployed across multiple departments to maximize utilization and justify expenditure.
Workflow Integration and Interoperability
Seamless integration into existing surgical workflows is critical for widespread adoption. AR guidance systems must interface with hospital information systems, imaging modalities, and surgical navigation platforms. Companies like Brainlab are focusing on open architecture and interoperability, enabling their AR solutions to work with third-party devices and data sources. In 2025, regulatory bodies are also emphasizing interoperability standards, which is expected to further facilitate integration and reduce workflow disruption.
Outlook
Looking ahead, the next few years are likely to see continued investment in user-friendly interfaces, automated calibration, and AI-driven workflow optimization. As more clinical evidence emerges demonstrating improved surgical accuracy and patient outcomes, reimbursement models may evolve to support AR adoption. Collaborative efforts between manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies will be essential to overcome remaining barriers and realize the full potential of AR surgical guidance systems.
Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Emerging Markets
The adoption and development of Augmented Reality (AR) surgical guidance systems are advancing rapidly across global regions, with North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and emerging markets each demonstrating distinct trajectories in 2025 and the near future.
- North America: The United States and Canada remain at the forefront of AR surgical guidance innovation and clinical integration. Major medical device manufacturers such as Medtronic and Smith & Nephew are actively commercializing AR-assisted navigation platforms for orthopedic, spine, and neurosurgical procedures. The FDA’s progressive stance on digital health technologies has enabled faster regulatory pathways, with several AR systems receiving clearance for intraoperative use. Leading academic hospitals and health systems are piloting AR for complex surgeries, and ongoing collaborations with technology firms are expected to further expand clinical applications through 2025.
- Europe: European adoption is driven by robust public healthcare investment and a strong focus on surgical precision and patient safety. Companies such as Brainlab (Germany) and Carl Zeiss Meditec (Germany) are prominent in developing and deploying AR navigation solutions, particularly in neurosurgery and ENT. The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) framework is shaping market entry, with a growing number of AR systems achieving CE marking. National health services in countries like Germany, France, and the UK are supporting pilot programs, and cross-border research initiatives are fostering innovation in AR-guided minimally invasive surgery.
- Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing accelerated growth, led by Japan, South Korea, China, and Australia. Japanese firms such as Olympus Corporation are investing in AR-enhanced endoscopic and laparoscopic platforms. In China, government-backed digital health initiatives and partnerships with global medtech leaders are driving rapid adoption in tertiary hospitals. South Korea’s advanced IT infrastructure supports integration of AR with robotic surgery systems. Regional demand is fueled by rising surgical volumes, increasing healthcare expenditure, and a focus on medical technology modernization.
- Emerging Markets: In Latin America, the Middle East, and parts of Southeast Asia, AR surgical guidance is in the early stages of adoption. Pilot projects are underway in major urban hospitals, often in collaboration with international device manufacturers. Cost constraints and limited digital infrastructure remain challenges, but technology transfer programs and public-private partnerships are expected to improve access. As device costs decrease and training programs expand, emerging markets are projected to see gradual uptake of AR surgical systems over the next several years.
Across all regions, the outlook for AR surgical guidance systems in 2025 and beyond is marked by increasing clinical validation, regulatory support, and integration with complementary technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence. The pace of adoption will vary, but global momentum is expected to accelerate as evidence of improved surgical outcomes and workflow efficiency continues to mount.
Future Outlook: Next-Gen AR, Market Opportunities, and Strategic Recommendations
The outlook for augmented reality (AR) surgical guidance systems in 2025 and the coming years is marked by rapid technological evolution, expanding clinical adoption, and intensifying competition among established medtech firms and innovative startups. As AR hardware matures—driven by lighter, more ergonomic headsets and improved spatial tracking—surgeons are increasingly able to overlay critical anatomical data directly onto the operative field, enhancing precision and reducing cognitive load.
Key industry players are accelerating the integration of AR into surgical workflows. Medtronic continues to advance its AR-enabled navigation platforms, focusing on spine and cranial procedures, while Smith+Nephew has expanded its AR portfolio for orthopedic applications, leveraging real-time visualization to improve implant alignment and outcomes. Siemens Healthineers is also investing in AR for image-guided interventions, aiming to streamline complex procedures and reduce intraoperative errors.
Recent clinical studies and pilot deployments in 2024 have demonstrated measurable benefits: AR guidance has been shown to reduce operative times, improve accuracy in screw placement, and decrease radiation exposure in minimally invasive surgeries. Hospitals adopting these systems report enhanced training for residents and improved patient engagement, as AR visualizations facilitate clearer communication of surgical plans.
Looking ahead, the next generation of AR surgical guidance will likely feature deeper integration with artificial intelligence (AI) for real-time decision support, as well as seamless connectivity with hospital information systems. Companies such as Philips are exploring cloud-based AR platforms that enable remote collaboration and tele-mentoring, expanding access to expert guidance in underserved regions.
Market opportunities are substantial, particularly in high-growth regions across Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where demand for advanced surgical technologies is rising. Strategic recommendations for stakeholders include:
- Investing in open, interoperable AR platforms to facilitate integration with diverse imaging modalities and surgical robots.
- Prioritizing user-centered design to ensure surgeon comfort and workflow compatibility, addressing barriers to adoption.
- Partnering with academic medical centers to generate robust clinical evidence and support regulatory approvals.
- Developing scalable training programs leveraging AR for both novice and experienced surgeons.
As AR surgical guidance systems continue to mature, the sector is poised for significant growth, with the potential to transform surgical practice, improve patient outcomes, and create new value streams for medtech innovators.
Sources & References
- Medtronic
- Smith+Nephew
- Brainlab
- Augmedics
- Microsoft
- Siemens Healthineers
- GE HealthCare
- Philips
- Intuitive Surgical
- IEEE
- ASTM International
- Carl Zeiss Meditec
- Olympus Corporation