Turbomolecular Vacuum Pump Manufacturing in 2025: Navigating Disruptive Technologies and Surging Global Demand. Explore the Key Drivers, Market Forecasts, and Strategic Opportunities Shaping the Industry’s Future.
- Executive Summary: 2025 Market Highlights and Key Takeaways
- Industry Overview: Turbomolecular Vacuum Pump Manufacturing Landscape
- Market Size & Growth Forecast (2025–2030): CAGR and Revenue Projections
- Key Application Sectors: Semiconductor, Analytical Instruments, and Beyond
- Technological Advancements: Next-Generation Pump Designs and Digital Integration
- Competitive Analysis: Leading Manufacturers and Strategic Moves
- Regional Trends: Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe Market Dynamics
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Pump Manufacturing
- Supply Chain, Raw Materials, and Regulatory Considerations
- Future Outlook: Disruptive Trends, Investment Opportunities, and Strategic Recommendations
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: 2025 Market Highlights and Key Takeaways
The turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing sector is poised for robust activity in 2025, driven by expanding demand from semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and advanced research applications. As global industries increasingly require ultra-high vacuum environments, manufacturers are scaling up production and investing in technological innovation to meet evolving performance and efficiency standards.
Key industry leaders such as Edwards Vacuum, Pfeiffer Vacuum, Atlas Copco (through its Leybold and Edwards brands), and ULVAC continue to dominate the market landscape. These companies are leveraging their global manufacturing footprints and R&D capabilities to introduce next-generation turbomolecular pumps with improved energy efficiency, lower vibration, and enhanced digital integration for predictive maintenance. For example, Pfeiffer Vacuum has recently expanded its production capacity in Europe to address surging demand from the semiconductor and coating industries, while Edwards Vacuum is focusing on smart pump technologies and sustainability initiatives.
The semiconductor sector remains the primary growth engine, with chip manufacturers ramping up investments in new fabs across Asia, North America, and Europe. This trend is expected to sustain high order volumes for turbomolecular pumps, which are critical for processes such as etching, deposition, and ion implantation. Additionally, the life sciences and analytical instrumentation markets are contributing to steady demand, as high-precision vacuum environments are essential for mass spectrometry and electron microscopy.
Supply chain resilience and localization are emerging as strategic priorities in 2025. Leading manufacturers are diversifying their supplier bases and investing in regional production hubs to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and logistics disruptions. ULVAC and Atlas Copco have both announced initiatives to strengthen their presence in key Asian and European markets, ensuring faster delivery times and tailored customer support.
Looking ahead, the outlook for turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing remains positive, with sustained double-digit growth anticipated in core application sectors. The industry is expected to see continued advancements in digitalization, energy efficiency, and materials engineering, positioning leading manufacturers to capture new opportunities in emerging fields such as quantum computing and advanced materials research.
Industry Overview: Turbomolecular Vacuum Pump Manufacturing Landscape
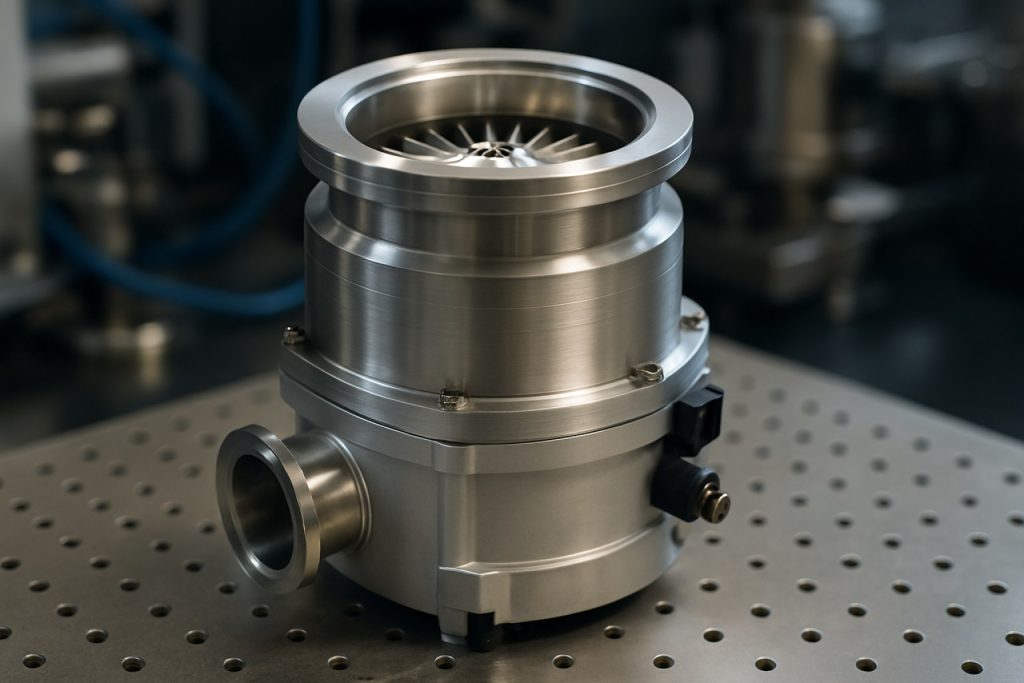
The turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing industry in 2025 is characterized by robust technological innovation, globalized supply chains, and increasing demand from high-precision sectors such as semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and advanced research. Turbomolecular pumps, essential for achieving ultra-high vacuum environments, are critical components in processes requiring contamination-free and particle-free atmospheres.
Leading manufacturers such as Edwards Vacuum, Pfeiffer Vacuum, Atlas Copco (through its Leybold and Edwards brands), ULVAC, and Shimadzu Corporation continue to dominate the global landscape. These companies invest heavily in R&D to improve pump efficiency, reliability, and integration with digital monitoring systems. For instance, Pfeiffer Vacuum has focused on smart pump technologies, enabling predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics, which are increasingly demanded by semiconductor and research clients.
The industry is witnessing a shift towards more compact, energy-efficient, and low-vibration designs, driven by the miniaturization of semiconductor devices and the expansion of analytical laboratories. Edwards Vacuum and ULVAC have both introduced new product lines in recent years that emphasize reduced power consumption and enhanced operational lifespans, responding to sustainability and cost-of-ownership concerns.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains a key growth region, propelled by the rapid expansion of semiconductor manufacturing in countries like China, South Korea, and Taiwan. Japanese manufacturers such as ULVAC and Shimadzu Corporation maintain strong regional presences, while European and US-based firms continue to supply high-end markets and collaborate with global OEMs.
Supply chain resilience and component sourcing have become focal points in the wake of recent global disruptions. Manufacturers are diversifying suppliers and investing in local production capabilities to mitigate risks. Additionally, environmental regulations and the push for greener manufacturing processes are influencing material choices and lifecycle management strategies across the sector.
Looking ahead, the turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing industry is expected to see continued growth through 2025 and beyond, fueled by ongoing investments in semiconductor fabs, quantum computing, and advanced materials research. The integration of digital technologies, sustainability initiatives, and regional manufacturing expansion will likely define the competitive landscape in the coming years.
Market Size & Growth Forecast (2025–2030): CAGR and Revenue Projections
The global turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing sector is poised for robust growth between 2025 and 2030, driven by expanding applications in semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and advanced research. As of 2025, the market is estimated to be valued in the low single-digit billions of USD, with leading manufacturers reporting strong order books and capacity expansions. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the period is widely projected to range between 5% and 7%, reflecting both organic demand and technological advancements.
Key players such as Pfeiffer Vacuum Technology AG, Edwards Vacuum (a division of Atlas Copco), and ULVAC, Inc. are investing in new production lines and R&D to address the increasing sophistication required by the semiconductor and electronics industries. For instance, Pfeiffer Vacuum Technology AG has reported double-digit growth in its vacuum solutions segment, attributing much of this to the surging demand for high-vacuum pumps in chip manufacturing and scientific research. Similarly, Edwards Vacuum continues to expand its global manufacturing footprint, with new facilities and upgrades aimed at increasing output and reducing lead times.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, South Korea, and Taiwan, is expected to remain the largest and fastest-growing market for turbomolecular vacuum pumps, owing to the concentration of semiconductor foundries and display panel manufacturers. Japanese manufacturers such as ULVAC, Inc. and Shimadzu Corporation are also scaling up production to meet regional and global demand. In Europe, Leybold GmbH (a subsidiary of Atlas Copco) and Pfeiffer Vacuum Technology AG are focusing on high-end applications, including particle accelerators and space research.
Looking ahead to 2030, the market outlook remains positive, underpinned by the ongoing miniaturization of electronic components, the proliferation of quantum computing research, and the expansion of clean energy technologies—all of which require advanced vacuum environments. The sector’s growth trajectory is further supported by continuous innovation in pump design, energy efficiency, and digital integration, as highlighted by the product development pipelines of major manufacturers. As a result, the turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing industry is expected to surpass USD 3 billion in annual revenues by 2030, with the potential for even higher growth if emerging applications accelerate.
Key Application Sectors: Semiconductor, Analytical Instruments, and Beyond
Turbomolecular vacuum pumps are critical components in high-vacuum environments, with their manufacturing closely tied to the evolving needs of several advanced technology sectors. As of 2025, the primary application sectors driving demand and innovation in turbomolecular pump manufacturing are the semiconductor industry, analytical instrumentation, and a range of emerging fields such as quantum computing and advanced materials research.
The semiconductor sector remains the largest and most influential market for turbomolecular pumps. The ongoing global expansion of semiconductor fabrication capacity—driven by the proliferation of AI, 5G, and automotive electronics—has led to increased investment in vacuum technology. Leading manufacturers such as Edwards Vacuum, Pfeiffer Vacuum, and ULVAC are scaling up production and introducing new models tailored for the stringent requirements of semiconductor manufacturing, including extreme cleanliness, reliability, and compatibility with corrosive process gases. For example, Edwards Vacuum has highlighted the importance of energy-efficient and low-maintenance pumps for next-generation chip fabrication plants.
Analytical instruments—such as mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, and surface analysis systems—constitute another significant application sector. The demand for higher sensitivity and faster analysis in life sciences, environmental monitoring, and materials science is pushing manufacturers to develop compact, low-vibration, and high-throughput turbomolecular pumps. Companies like Pfeiffer Vacuum and Leybold are actively collaborating with instrument makers to integrate advanced pump technologies that enable more precise and reliable measurements.
Beyond these established markets, new application areas are emerging. Quantum computing research, for instance, requires ultra-high vacuum environments for the manipulation of quantum bits, spurring demand for specialized turbomolecular pumps. Similarly, the development of advanced materials—such as 2D materials and nanostructures—relies on vacuum deposition and analysis techniques that benefit from the latest pump innovations. Manufacturers are responding by investing in R&D and expanding their product portfolios to address these niche but rapidly growing sectors.
Looking ahead, the outlook for turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing is robust. The convergence of semiconductor industry growth, the miniaturization of analytical instruments, and the rise of new high-tech applications is expected to sustain strong demand and drive further technological advancements. Leading companies are likely to continue investing in automation, digitalization, and sustainability initiatives to meet the evolving needs of these key sectors.
Technological Advancements: Next-Generation Pump Designs and Digital Integration
The turbomolecular vacuum pump sector is experiencing a wave of technological advancements in 2025, driven by the demands of semiconductor manufacturing, analytical instrumentation, and advanced research applications. Next-generation pump designs are increasingly focused on higher efficiency, reduced footprint, and enhanced integration with digital monitoring systems. Leading manufacturers are leveraging innovations in rotor dynamics, materials science, and smart control electronics to deliver pumps that meet the stringent requirements of modern vacuum-dependent industries.
A key trend is the adoption of advanced rotor and bearing technologies. Magnetic levitation (maglev) bearings, for example, are being refined to minimize mechanical wear, reduce vibration, and extend maintenance intervals. Companies such as Pfeiffer Vacuum and Edwards Vacuum have introduced maglev-based turbomolecular pumps that offer improved reliability and lower total cost of ownership. These designs are particularly valuable in cleanroom environments, where contamination and downtime must be minimized.
Materials innovation is also shaping next-generation pumps. The use of high-strength, lightweight alloys and advanced coatings enables higher rotational speeds and improved corrosion resistance. Leybold and ULVAC are among the manufacturers investing in proprietary materials and surface treatments to enhance pump durability and performance, especially for aggressive process gases encountered in semiconductor and thin-film applications.
Digital integration is another defining feature of 2025’s turbomolecular pump manufacturing. Smart pumps equipped with embedded sensors and IoT connectivity allow for real-time monitoring of parameters such as vibration, temperature, and rotational speed. This data can be accessed remotely, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime. Atlas Copco (parent company of Edwards Vacuum) and Pfeiffer Vacuum have both launched digital platforms that integrate pump diagnostics with broader factory automation systems, supporting Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Looking ahead, the outlook for turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing is shaped by the continued miniaturization of electronics, the expansion of quantum computing research, and the growth of advanced materials processing. Manufacturers are expected to further enhance energy efficiency, noise reduction, and digital service offerings. As the industry moves toward more autonomous and connected production environments, the integration of artificial intelligence for predictive analytics and process optimization is likely to become a standard feature in next-generation pump systems.
Competitive Analysis: Leading Manufacturers and Strategic Moves
The turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing sector in 2025 is characterized by intense competition among a handful of global leaders, each leveraging advanced engineering, strategic acquisitions, and regional expansion to maintain or grow their market share. The industry is driven by demand from semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and research applications, with manufacturers focusing on innovation, reliability, and energy efficiency.
Among the most prominent players, Edwards Vacuum (a subsidiary of Atlas Copco) continues to be a dominant force, with a broad portfolio of turbomolecular pumps tailored for semiconductor and scientific markets. Edwards has invested heavily in R&D, particularly in developing pumps with lower vibration and improved contamination control, responding to the stringent requirements of next-generation chip manufacturing. The company’s global manufacturing footprint, including facilities in the UK, Czech Republic, and Asia, supports its ability to serve both established and emerging markets.
Another key competitor, Pfeiffer Vacuum, headquartered in Germany, is renowned for its high-performance turbopumps and integrated vacuum solutions. Pfeiffer has recently expanded its production capacity in Europe and China, aiming to reduce lead times and better serve the rapidly growing Asian semiconductor sector. The company’s strategic focus includes digitalization of pump monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing value for customers in high-throughput environments.
Japanese manufacturer ULVAC is also a significant player, with a strong presence in Asia and a growing footprint in North America and Europe. ULVAC’s strategy emphasizes vertical integration, producing not only pumps but also vacuum systems and related components, which allows for greater control over quality and supply chain resilience. The company is investing in next-generation pump designs to address the miniaturization trends in electronics manufacturing.
Other notable manufacturers include Shimadzu Corporation, which leverages its expertise in analytical instrumentation to develop specialized turbomolecular pumps for mass spectrometry and electron microscopy, and Agilent Technologies, which focuses on compact, high-speed pumps for laboratory and industrial applications. Both companies are enhancing their product lines with features such as remote diagnostics and energy-efficient operation.
Looking ahead, the competitive landscape is expected to see further consolidation, with leading manufacturers pursuing mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships to expand their technological capabilities and global reach. The ongoing shift toward smart manufacturing and the increasing complexity of end-user requirements will likely drive continued investment in R&D and digital solutions, reinforcing the position of established players while creating opportunities for innovative entrants.
Regional Trends: Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe Market Dynamics
The global turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing sector is experiencing dynamic regional shifts, with Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe each playing distinct roles in shaping the industry’s trajectory through 2025 and beyond. These regions are influenced by their respective industrial bases, technological capabilities, and strategic investments in high-vacuum applications such as semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and advanced research.
Asia-Pacific continues to assert its dominance, driven primarily by the rapid expansion of the semiconductor and electronics industries in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. The region is home to major manufacturing hubs and is witnessing significant investments in new fabrication plants (“fabs”) and R&D facilities. Companies such as ULVAC, Inc. (Japan) and Edwards Vacuum (with substantial operations in Asia) are expanding their production capacities and localizing supply chains to meet the surging demand for high-performance vacuum solutions. The Chinese market, in particular, is seeing increased domestic production and government support for advanced manufacturing, further boosting regional output and innovation.
North America remains a critical market, underpinned by its leadership in semiconductor technology, aerospace, and scientific research. The United States, in particular, is investing heavily in reshoring semiconductor manufacturing and strengthening its supply chain resilience. Companies like Pfeiffer Vacuum (with a strong U.S. presence) and Edwards Vacuum are supporting these initiatives by enhancing local manufacturing capabilities and service networks. The region’s focus on advanced R&D, including quantum computing and materials science, continues to drive demand for high-precision turbomolecular pumps.
Europe maintains its reputation for engineering excellence and innovation in vacuum technology. German-based Pfeiffer Vacuum and Leybold GmbH are at the forefront, supplying pumps for semiconductor, pharmaceutical, and scientific applications. The European Union’s emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency is prompting manufacturers to develop more efficient, lower-emission pump technologies. Additionally, Europe’s robust research infrastructure and collaborations with universities and institutes are fostering ongoing advancements in vacuum science.
Looking ahead, regional dynamics are expected to intensify as governments and industry players invest in next-generation manufacturing and research. Asia-Pacific is likely to further consolidate its manufacturing leadership, while North America and Europe focus on high-value applications and technological innovation. Strategic partnerships, local production, and R&D investments will be key differentiators in the evolving global landscape of turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Pump Manufacturing
Sustainability and energy efficiency have become central themes in the manufacturing of turbomolecular vacuum pumps, especially as the industry faces increasing regulatory and customer-driven demands for greener solutions. In 2025 and the coming years, leading manufacturers are intensifying their focus on reducing the environmental impact of both their products and production processes.
A key trend is the integration of energy-efficient motor technologies and advanced control systems. For example, Pfeiffer Vacuum has developed turbomolecular pumps with intelligent drive electronics that optimize power consumption based on real-time demand, significantly reducing energy usage during operation. Similarly, Edwards Vacuum emphasizes the use of brushless DC motors and variable speed drives in their latest pump models, which not only lower energy consumption but also extend service intervals, reducing waste and resource use.
Manufacturers are also re-evaluating materials and production methods. Leybold has implemented closed-loop recycling systems for metals and plastics used in pump components, aiming to minimize raw material extraction and associated emissions. Additionally, the company is investing in renewable energy sources for its manufacturing facilities, targeting a substantial reduction in its carbon footprint over the next few years.
Product lifecycle considerations are increasingly important. Companies like ULVAC are designing pumps for easier disassembly and recycling at end-of-life, and offering refurbishment programs to extend product longevity. This approach not only conserves resources but also aligns with circular economy principles, which are gaining traction across the vacuum technology sector.
Industry-wide, there is a push to comply with and exceed international standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. Many manufacturers are publishing annual sustainability reports and setting ambitious targets for emissions reduction, waste minimization, and energy efficiency. These initiatives are often driven by both internal corporate responsibility goals and external pressures from semiconductor, research, and industrial customers who increasingly require sustainable supply chains.
Looking ahead, the outlook for sustainability in turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing is positive. Continued investment in R&D is expected to yield further improvements in pump efficiency, materials selection, and manufacturing processes. As regulatory frameworks tighten and market expectations evolve, the sector is poised to deliver more environmentally responsible solutions without compromising on performance or reliability.
Supply Chain, Raw Materials, and Regulatory Considerations
The supply chain for turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing in 2025 is characterized by a complex network of precision engineering firms, specialty materials suppliers, and advanced electronics manufacturers. The core components—rotors, stators, high-speed bearings, and drive electronics—require ultra-high purity metals and alloys, such as stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum, as well as ceramics and specialized polymers for insulation and sealing. The ongoing global focus on semiconductor, pharmaceutical, and research sectors continues to drive demand for these pumps, intensifying competition for high-grade raw materials.
Key manufacturers such as Pfeiffer Vacuum, Edwards Vacuum, and Atlas Copco (through its Leybold and Edwards brands) maintain vertically integrated supply chains to ensure quality and traceability of critical components. These companies often source raw materials from established suppliers in Europe, Japan, and the United States, but recent geopolitical tensions and logistical disruptions have prompted a shift toward regionalization and dual sourcing strategies. For example, Pfeiffer Vacuum has expanded its European manufacturing footprint to mitigate risks associated with global shipping delays and raw material shortages.
The electronics and control systems integral to turbomolecular pumps rely on advanced semiconductors and microcontrollers, which have been subject to global shortages since 2021. While the situation is gradually improving, manufacturers are investing in closer partnerships with electronics suppliers and, in some cases, developing in-house capabilities to reduce dependency on external sources. Edwards Vacuum has reported increased collaboration with local electronics firms to secure supply and accelerate innovation in digital pump controls.
Regulatory considerations are increasingly shaping the supply chain landscape. Compliance with the European Union’s REACH regulations, RoHS directives, and similar standards in North America and Asia is mandatory, particularly regarding hazardous substances and environmental impact. Manufacturers are investing in greener production processes and recyclable materials to meet both regulatory requirements and customer expectations for sustainability. Atlas Copco has publicly committed to reducing the carbon footprint of its vacuum products, including turbomolecular pumps, by optimizing energy efficiency and material usage.
Looking ahead, the outlook for the supply chain in turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing is cautiously optimistic. While raw material price volatility and regulatory pressures persist, the industry’s move toward digitalization, regional supply networks, and sustainable practices is expected to enhance resilience and competitiveness over the next few years.
Future Outlook: Disruptive Trends, Investment Opportunities, and Strategic Recommendations
The turbomolecular vacuum pump manufacturing sector is poised for significant transformation in 2025 and the coming years, driven by technological innovation, evolving end-user demands, and strategic investments. As industries such as semiconductor fabrication, analytical instrumentation, and advanced materials research continue to demand higher vacuum performance and reliability, manufacturers are responding with disruptive trends and new business strategies.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of smart technologies and digitalization into turbomolecular pump systems. Leading manufacturers like Edwards Vacuum and Pfeiffer Vacuum are investing in pumps equipped with advanced sensors, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These features not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce downtime and total cost of ownership for end-users, making them attractive in high-throughput environments such as semiconductor fabs.
Sustainability is another key driver shaping the future of turbomolecular pump manufacturing. Companies are increasingly focusing on energy-efficient designs and the use of recyclable materials. For instance, Leybold has highlighted its commitment to reducing the environmental impact of its vacuum solutions, aligning with broader industry trends toward greener manufacturing processes. This focus is expected to intensify as regulatory pressures and customer expectations around sustainability grow.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains a focal point for investment, with countries like China, South Korea, and Taiwan expanding their semiconductor and electronics manufacturing capacities. This regional growth is prompting global players such as ULVAC and Shimadzu Corporation to strengthen their local manufacturing and service networks, ensuring rapid response to customer needs and capturing emerging market share.
Strategically, mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are expected to accelerate as companies seek to broaden their technology portfolios and global reach. The recent trend of established vacuum technology firms collaborating with automation and digital solution providers is likely to continue, fostering innovation and enabling the development of next-generation turbomolecular pumps.
For investors and stakeholders, the sector offers compelling opportunities, particularly in companies that demonstrate agility in adopting digitalization, sustainability, and regional expansion strategies. To remain competitive, manufacturers should prioritize R&D in smart pump technologies, invest in sustainable manufacturing practices, and pursue strategic alliances that enhance their value proposition in high-growth markets.