Wearable Gesture Recognition Systems in 2025: Transforming Human-Device Interaction and Unlocking New Market Frontiers. Explore the Technologies, Trends, and Forecasts Shaping the Next Five Years.
- Executive Summary: Key Insights and 2025 Outlook
- Market Size and Growth Forecast (2025–2030): CAGR and Revenue Projections
- Core Technologies: Sensors, AI Algorithms, and Haptic Feedback
- Leading Players and Strategic Initiatives (e.g., apple.com, sony.com, microsoft.com)
- Emerging Applications: Healthcare, Gaming, AR/VR, and Industrial Use Cases
- Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of World
- Competitive Landscape and Recent Partnerships
- Challenges: Technical Barriers, Privacy, and User Adoption
- Regulatory Environment and Industry Standards (e.g., ieee.org)
- Future Outlook: Disruptive Innovations and Long-Term Market Potential
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: Key Insights and 2025 Outlook
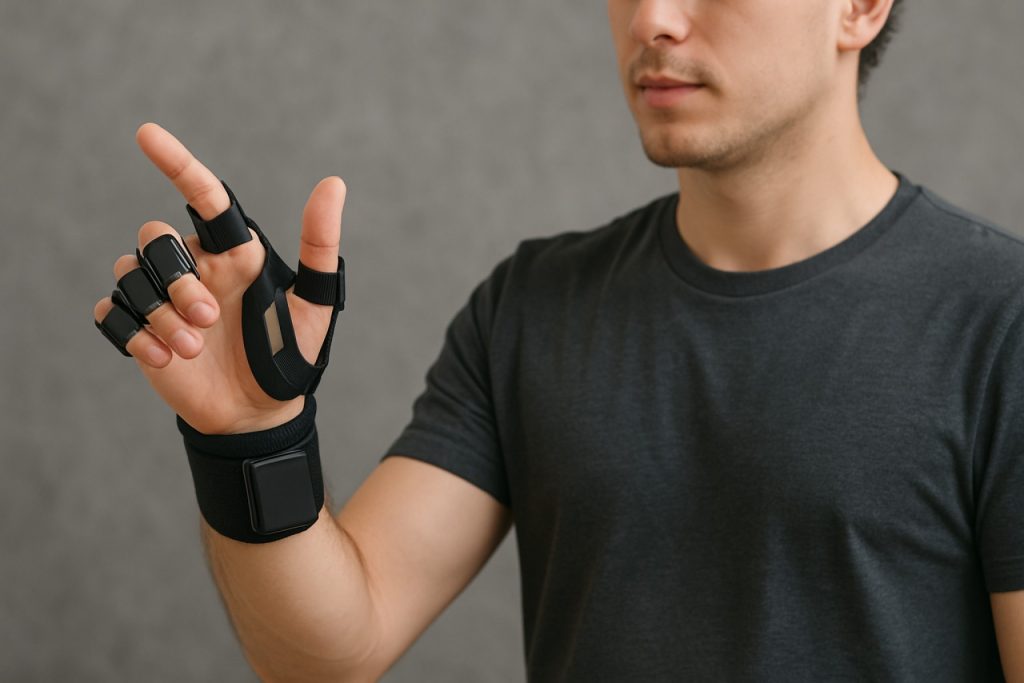
Wearable gesture recognition systems are rapidly advancing as a cornerstone technology in human-computer interaction, enabling intuitive control of devices through natural body movements. In 2025, the sector is characterized by robust innovation, expanding applications, and increasing integration with consumer electronics, healthcare, and industrial automation. Key players are leveraging advances in sensor miniaturization, machine learning, and wireless connectivity to deliver more accurate, responsive, and user-friendly solutions.
Major technology companies are driving the adoption of gesture recognition wearables. Sony Corporation continues to refine its motion-sensing platforms, building on its experience with gaming and entertainment devices. Samsung Electronics is integrating gesture recognition into its smartwatches and fitness trackers, enhancing user interaction and accessibility. Apple Inc. is also exploring gesture-based controls in its wearable ecosystem, with patents and developer resources indicating ongoing research and potential product integration.
Specialized firms are pushing the boundaries of gesture recognition hardware and software. Ultraleap (formerly Leap Motion) is a leader in hand-tracking and mid-air gesture control, supplying technology for AR/VR headsets and industrial interfaces. Noitom Ltd. focuses on motion capture wearables for animation, healthcare, and robotics, while Xsens Technologies provides inertial sensor-based systems for precise gesture tracking in professional and research settings.
In 2025, the convergence of artificial intelligence and edge computing is enabling real-time gesture recognition with lower latency and improved energy efficiency. Wearable devices are increasingly capable of processing complex gestures locally, reducing reliance on cloud connectivity and enhancing privacy. This is particularly relevant in healthcare, where gesture recognition is being used for rehabilitation, remote monitoring, and assistive technologies for individuals with disabilities.
Looking ahead, the outlook for wearable gesture recognition systems is strong. The proliferation of AR/VR devices, the rise of smart home ecosystems, and the growing demand for touchless interfaces in public and industrial environments are expected to drive further adoption. Industry collaborations and open development platforms are accelerating innovation, while regulatory focus on data privacy and device interoperability is shaping product design and deployment.
- Key companies: Sony Corporation, Samsung Electronics, Apple Inc., Ultraleap, Noitom Ltd., Xsens Technologies
- 2025 focus: Enhanced accuracy, real-time processing, expanded healthcare and AR/VR applications
- Outlook: Continued growth driven by consumer, medical, and industrial demand; emphasis on privacy, interoperability, and user experience
Market Size and Growth Forecast (2025–2030): CAGR and Revenue Projections
The market for wearable gesture recognition systems is poised for robust growth between 2025 and 2030, driven by advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and the proliferation of smart devices across consumer, industrial, and healthcare sectors. As of 2025, the sector is witnessing increased adoption of gesture-based interfaces in smartwatches, fitness trackers, augmented reality (AR) headsets, and specialized industrial wearables. This trend is underpinned by the demand for more intuitive, hands-free user experiences and the integration of gesture recognition into mainstream consumer electronics.
Key industry players such as Sony Corporation, Samsung Electronics, and Microsoft Corporation are actively developing and commercializing wearable devices with advanced gesture recognition capabilities. For instance, Sony Corporation has invested in motion-sensing technologies for its wearables and AR products, while Samsung Electronics continues to enhance gesture-based controls in its Galaxy Watch series and other smart devices. Microsoft Corporation has also integrated gesture recognition into its HoloLens mixed reality platform, targeting both enterprise and consumer applications.
From a revenue perspective, the global wearable gesture recognition systems market is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the high single to low double digits over the 2025–2030 period. This growth is fueled by expanding use cases in healthcare—such as rehabilitation and remote patient monitoring—where companies like Xsens Technologies and Myo (Thalmic Labs) are notable for their motion capture and electromyography-based gesture solutions. Additionally, the industrial sector is adopting gesture-controlled wearables for safety and productivity, with firms like ProGlove providing smart gloves that enable hands-free operation in logistics and manufacturing environments.
Looking ahead, the market outlook remains positive as hardware miniaturization, improved battery life, and the integration of machine learning algorithms enhance the accuracy and usability of gesture recognition systems. The expansion of 5G networks and edge computing is expected to further accelerate adoption by enabling real-time processing and seamless connectivity. As a result, industry analysts anticipate that the wearable gesture recognition systems market will reach multi-billion-dollar annual revenues by 2030, with North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific emerging as key growth regions.
Core Technologies: Sensors, AI Algorithms, and Haptic Feedback
Wearable gesture recognition systems are rapidly advancing, driven by innovations in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, and haptic feedback mechanisms. As of 2025, these core technologies are converging to enable more accurate, intuitive, and immersive user experiences across consumer electronics, healthcare, industrial, and gaming sectors.
Sensor technology forms the backbone of gesture recognition wearables. Modern systems increasingly utilize a combination of inertial measurement units (IMUs), electromyography (EMG) sensors, optical sensors, and capacitive touch arrays. Companies like STMicroelectronics and Analog Devices are prominent suppliers of MEMS-based accelerometers and gyroscopes, which are essential for tracking hand and arm movements with high precision. EMG sensors, which detect electrical activity from muscle contractions, are being integrated into wearable bands and gloves, as seen in products from Thalmic Labs (now North, acquired by Google) and Bioservo Technologies. Optical and time-of-flight sensors, such as those developed by Infineon Technologies, are also being adopted for contactless gesture tracking, particularly in AR/VR headsets and smart glasses.
AI algorithms are central to interpreting complex sensor data and translating it into actionable commands. Recent advances in deep learning and edge AI have enabled real-time gesture recognition with minimal latency and improved accuracy. Companies like Qualcomm and NVIDIA are embedding dedicated AI accelerators in wearable chipsets, allowing for on-device processing that preserves user privacy and reduces reliance on cloud connectivity. Open-source frameworks and toolkits, such as TensorFlow Lite and PyTorch Mobile, are also being optimized for wearable platforms, facilitating rapid prototyping and deployment of custom gesture recognition models.
Haptic feedback is increasingly integrated into gesture recognition wearables to provide users with tactile responses, enhancing immersion and usability. Immersion Corporation is a leader in haptic technology, licensing its solutions to manufacturers of smartwatches, AR/VR controllers, and exoskeleton gloves. Advanced haptic actuators, including piezoelectric and electroactive polymer-based devices, are being miniaturized for seamless integration into lightweight wearables. This trend is expected to accelerate as demand grows for more natural and responsive user interfaces in spatial computing and remote collaboration.
Looking ahead, the next few years will likely see further miniaturization of sensors, greater energy efficiency, and the proliferation of multimodal systems that combine gesture, voice, and eye tracking. Industry collaborations and standardization efforts, such as those led by the Bluetooth SIG and IEEE, are expected to drive interoperability and accelerate adoption across diverse application domains.
Leading Players and Strategic Initiatives (e.g., apple.com, sony.com, microsoft.com)
The wearable gesture recognition systems market in 2025 is characterized by rapid innovation and strategic positioning among leading technology companies. Major players are leveraging their expertise in hardware, software, and artificial intelligence to develop intuitive, hands-free interfaces for consumer electronics, healthcare, gaming, and industrial applications.
Apple Inc. continues to be a dominant force, integrating gesture recognition into its expanding ecosystem of wearables. The Apple Watch and Vision Pro headset exemplify the company’s commitment to natural user interfaces, with advanced sensors and machine learning enabling hand and finger gesture controls. Apple’s strategic focus on privacy and seamless integration across devices positions it as a leader in both consumer adoption and developer engagement.
Microsoft Corporation is advancing gesture recognition through its Microsoft HoloLens mixed reality platform. The HoloLens 2, for example, features sophisticated hand-tracking and spatial mapping, allowing users to interact with digital content in three dimensions. Microsoft’s partnerships with enterprise clients in manufacturing, healthcare, and education are driving adoption of gesture-based controls for productivity and training applications.
Sony Group Corporation is leveraging its expertise in sensors and entertainment to push the boundaries of gesture recognition in gaming and virtual reality. The Sony PlayStation VR2 system incorporates advanced motion tracking and haptic feedback, enabling more immersive and responsive gameplay. Sony’s ongoing investment in sensor technology and developer tools is expected to further enhance gesture-based experiences in upcoming product releases.
Other notable players include Samsung Electronics, which integrates gesture recognition into its Galaxy wearable devices, and Huawei Technologies, which is developing AI-powered gesture controls for smartwatches and AR glasses. Both companies are focusing on health monitoring and smart home integration as key growth areas.
Strategic initiatives across the sector include increased investment in AI algorithms for more accurate gesture detection, collaborations with academic institutions for research, and the development of open platforms to encourage third-party innovation. As hardware miniaturization and battery efficiency improve, leading companies are expected to introduce new form factors and expand gesture recognition capabilities into broader applications, including automotive interfaces and assistive technologies.
Looking ahead, the competitive landscape will be shaped by the ability of these companies to deliver seamless, secure, and context-aware gesture recognition experiences, with a strong emphasis on user privacy and cross-device interoperability.
Emerging Applications: Healthcare, Gaming, AR/VR, and Industrial Use Cases
Wearable gesture recognition systems are rapidly expanding their footprint across multiple sectors, with 2025 marking a pivotal year for their integration into healthcare, gaming, AR/VR, and industrial environments. These systems, which interpret human gestures via sensors embedded in wearables, are enabling more intuitive and immersive human-machine interactions.
In healthcare, gesture recognition wearables are being leveraged for rehabilitation, remote patient monitoring, and assistive technologies. Devices such as smart gloves and sensor-embedded bands allow clinicians to track patient movements with high precision, supporting post-stroke rehabilitation and physical therapy. Companies like Samsung Electronics and Sony Group Corporation are actively developing wearable platforms that integrate gesture recognition for health monitoring and accessibility, with ongoing collaborations with medical institutions to validate clinical efficacy.
The gaming industry continues to be a major driver for gesture-based wearables, with 2025 seeing a surge in demand for more immersive and responsive experiences. Gesture recognition gloves and wristbands are being adopted by leading console and PC gaming ecosystems, allowing players to interact naturally within virtual environments. Microsoft Corporation and Sony Group Corporation are both investing in next-generation controllers and wearables that utilize advanced motion tracking and haptic feedback, aiming to blur the line between physical and digital play.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications are also benefiting from advances in wearable gesture recognition. In 2025, AR/VR headsets and accessories are increasingly incorporating gesture sensors to enable touchless control, object manipulation, and enhanced user immersion. Meta Platforms, Inc. (formerly Facebook) is at the forefront, with its Reality Labs division developing wrist-worn devices that interpret neural signals and hand gestures for seamless AR/VR interaction. Similarly, Apple Inc. is rumored to be integrating gesture recognition into its upcoming spatial computing devices, further fueling competition and innovation in this space.
Industrial use cases are emerging as a significant growth area, with gesture recognition wearables being deployed for hands-free control of machinery, worker safety monitoring, and training simulations. Companies such as Honeywell International Inc. and Robert Bosch GmbH are piloting smart gloves and wristbands in manufacturing and logistics settings, aiming to improve operational efficiency and reduce workplace accidents. These deployments are expected to scale in the coming years as enterprises seek to digitize workflows and enhance worker ergonomics.
Looking ahead, the convergence of AI, miniaturized sensors, and wireless connectivity is set to accelerate the adoption of wearable gesture recognition systems across these sectors. As device accuracy and comfort improve, and as industry leaders continue to invest in ecosystem development, the next few years will likely see these technologies become integral to daily life and work.
Regional Analysis: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of World
The global landscape for wearable gesture recognition systems in 2025 is marked by dynamic regional trends, driven by technological innovation, consumer adoption, and industry partnerships. North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World each present distinct opportunities and challenges for market participants.
North America remains a leading hub for wearable gesture recognition, propelled by the presence of major technology companies and a robust ecosystem for innovation. Companies such as Apple Inc. and Microsoft Corporation continue to integrate advanced gesture recognition into their wearable devices, including smartwatches and mixed reality headsets. The region benefits from high consumer awareness, strong investment in R&D, and early adoption in sectors like healthcare, gaming, and enterprise productivity. In 2025, North American firms are expected to further expand gesture-based controls in AR/VR applications and fitness wearables, leveraging AI and sensor fusion for improved accuracy.
Europe is characterized by a focus on privacy, regulatory compliance, and cross-industry collaboration. Companies such as Infineon Technologies AG are advancing gesture recognition through radar and sensor technologies, with applications in automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics. The European market is also seeing increased adoption in healthcare and assistive technologies, supported by public funding and partnerships with research institutions. The region’s emphasis on data protection and user-centric design is shaping the development and deployment of gesture recognition systems, particularly in Germany, France, and the Nordic countries.
Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid growth, driven by manufacturing capabilities, a large consumer base, and government initiatives supporting digital transformation. Companies such as Sony Group Corporation and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. are at the forefront, integrating gesture recognition into smartwatches, smartphones, and AR devices. China, Japan, and South Korea are leading the region, with local startups and established firms collaborating on AI-powered gesture interfaces for gaming, education, and smart home applications. The Asia-Pacific market is expected to see the fastest adoption rates through 2025, fueled by affordable devices and expanding 5G infrastructure.
Rest of the World encompasses emerging markets in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, where adoption is gradually increasing. While infrastructure and affordability remain challenges, local innovation and partnerships with global technology providers are enabling pilot projects in healthcare, education, and public safety. As device costs decrease and connectivity improves, these regions are poised for incremental growth in wearable gesture recognition systems over the next few years.
Competitive Landscape and Recent Partnerships
The competitive landscape for wearable gesture recognition systems in 2025 is characterized by rapid innovation, strategic partnerships, and increasing convergence between hardware, software, and artificial intelligence. Major technology companies, established electronics manufacturers, and emerging startups are all vying for leadership in this dynamic sector.
Key players such as Sony Corporation, Samsung Electronics, and Microsoft Corporation continue to invest heavily in gesture recognition technologies, integrating them into smartwatches, AR/VR headsets, and fitness trackers. Sony, for example, has advanced its motion-sensing platforms for both consumer and professional applications, leveraging its expertise in sensors and gaming. Samsung has expanded its Galaxy wearable ecosystem with enhanced gesture controls, focusing on seamless user experiences and health monitoring. Microsoft, meanwhile, has incorporated gesture recognition into its HoloLens mixed reality devices, targeting enterprise and industrial use cases.
In the startup arena, companies like Ultraleap (formerly Leap Motion) are pushing the boundaries of touchless interaction through advanced hand-tracking and mid-air gesture recognition. Ultraleap’s technology is being adopted in automotive, retail, and immersive entertainment, often through collaborations with larger OEMs. Another notable entrant, Noitom Ltd., specializes in motion capture and gesture-based input devices, with a focus on virtual production and education.
Recent years have seen a surge in partnerships aimed at accelerating product development and market adoption. In 2024, Infineon Technologies AG partnered with Google to integrate radar-based gesture sensing into consumer devices, building on the Soli project’s momentum. This collaboration is expected to yield new gesture-enabled wearables and smart home products in 2025 and beyond. Similarly, STMicroelectronics has teamed up with leading wearable brands to supply low-power, high-precision sensors for gesture recognition, supporting both fitness and medical applications.
- Automotive suppliers such as Continental AG are working with gesture tech firms to bring intuitive controls to in-car infotainment and driver assistance systems.
- Healthcare device manufacturers are collaborating with gesture recognition specialists to enable touchless patient monitoring and rehabilitation tools.
- AR/VR platform providers are forming alliances with sensor and AI companies to deliver more immersive, gesture-driven experiences.
Looking ahead, the competitive landscape is expected to intensify as more companies enter the market and existing players deepen their partnerships. The focus will likely shift toward miniaturization, energy efficiency, and the integration of multimodal sensing (combining gesture, voice, and eye tracking). As interoperability standards mature, cross-industry collaborations will play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of wearable gesture recognition systems.
Challenges: Technical Barriers, Privacy, and User Adoption
Wearable gesture recognition systems, which interpret human gestures through sensors embedded in wearable devices, are advancing rapidly but face several significant challenges as of 2025. These challenges span technical barriers, privacy concerns, and issues related to user adoption, all of which will shape the trajectory of the sector in the coming years.
Technical Barriers remain a primary concern. Achieving high accuracy in gesture recognition is complicated by factors such as sensor noise, variability in user physiology, and environmental interference. Leading manufacturers like Sony Corporation and Samsung Electronics have made strides in miniaturizing and improving the sensitivity of inertial measurement units (IMUs) and electromyography (EMG) sensors, but real-time processing and power efficiency are still limiting factors. Battery life is a persistent issue, especially for always-on systems, and balancing computational demands with wearable form factors remains a technical hurdle. Furthermore, interoperability between devices and platforms is not yet standardized, complicating integration with broader Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems.
Privacy is an escalating concern as wearable gesture recognition systems collect and process sensitive biometric and behavioral data. Companies such as Apple Inc. and Meta Platforms, Inc. (formerly Facebook) have introduced privacy features in their wearable products, but the risk of unauthorized data access or misuse persists. The continuous monitoring required for gesture recognition can expose users to potential surveillance or profiling. Regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), are prompting manufacturers to implement stronger data protection measures, but global harmonization of privacy standards is still lacking. As more health-related and personal data are processed on-device, ensuring secure data transmission and storage will be critical.
User Adoption is influenced by both technical and social factors. While early adopters and technology enthusiasts have embraced gesture-controlled wearables, mainstream acceptance is hindered by concerns over device comfort, reliability, and perceived utility. Companies like Fitbit (now part of Google) and Garmin Ltd. are working to improve ergonomics and user experience, but skepticism remains regarding the necessity and accuracy of gesture-based controls. Additionally, cultural differences in gesture interpretation and the learning curve associated with new interaction paradigms can slow adoption rates. Over the next few years, industry players are expected to focus on refining user interfaces, expanding gesture vocabularies, and demonstrating clear value propositions to drive broader market penetration.
In summary, while wearable gesture recognition systems are poised for growth, overcoming technical, privacy, and adoption challenges will be essential for realizing their full potential in the near future.
Regulatory Environment and Industry Standards (e.g., ieee.org)
The regulatory environment and industry standards for wearable gesture recognition systems are rapidly evolving as these technologies become increasingly integrated into consumer electronics, healthcare, automotive, and industrial applications. In 2025, the focus is on ensuring interoperability, safety, privacy, and reliability, with several key organizations and industry consortia shaping the landscape.
A central role is played by the IEEE, which continues to develop and update standards relevant to wearable devices and gesture recognition. The IEEE 802.15 family, originally designed for wireless personal area networks, is being extended to address low-latency, high-reliability communication needs of gesture-based wearables. Additionally, the IEEE 11073 series, which covers personal health data communication, is increasingly relevant as gesture recognition is adopted in medical wearables for patient monitoring and rehabilitation.
Interoperability and data exchange are also addressed by the Bluetooth SIG, whose Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) specifications are widely adopted in gesture recognition wearables for efficient wireless communication. The 2024 release of Bluetooth Core Specification 5.4 introduced enhanced features for device synchronization and broadcast, directly benefiting multi-device gesture recognition scenarios.
On the privacy and data protection front, regulatory frameworks such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) continue to influence device design and data handling practices. Manufacturers like Sony Group Corporation and Samsung Electronics are implementing on-device processing and encrypted data transmission to comply with these regulations, especially as gesture data can be sensitive and personally identifiable.
Safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards are enforced by international bodies such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards ensure that wearable gesture recognition systems do not interfere with other electronic devices and are safe for prolonged human contact.
Looking ahead, industry groups such as the Open Connectivity Foundation are working on frameworks to enable seamless integration of gesture recognition wearables with smart home and IoT ecosystems. The next few years are expected to see further harmonization of standards, particularly around AI-driven gesture recognition algorithms, as well as increased regulatory scrutiny on biometric data usage. This evolving landscape will require manufacturers and developers to stay agile and proactive in compliance and certification processes.
Future Outlook: Disruptive Innovations and Long-Term Market Potential
The future of wearable gesture recognition systems is poised for significant transformation, driven by advances in sensor miniaturization, artificial intelligence, and integration with broader digital ecosystems. As of 2025, the sector is witnessing a convergence of hardware and software innovations that are expected to disrupt traditional human-computer interaction paradigms and unlock new market opportunities across industries.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of advanced machine learning algorithms directly onto wearable devices, enabling real-time gesture recognition with minimal latency and improved accuracy. Companies such as Apple Inc. and Samsung Electronics are at the forefront, embedding sophisticated gesture controls into their smartwatches and augmented reality (AR) headsets. For example, Apple’s recent iterations of the Apple Watch and Vision Pro headset leverage a combination of inertial sensors, optical cameras, and neural processing units to interpret complex hand and finger movements, allowing users to interact with digital content without physical touch.
In parallel, startups and established players are exploring new form factors beyond wrist-worn devices. Glove-based systems, such as those developed by HaptX Inc., offer high-fidelity gesture tracking and haptic feedback, targeting applications in virtual reality (VR) training, remote robotics, and healthcare rehabilitation. Meanwhile, companies like Sony Group Corporation are investing in gesture recognition for gaming and immersive media, with their PlayStation VR ecosystem incorporating hand-tracking capabilities to enhance user engagement.
The automotive sector is also emerging as a key adopter, with manufacturers such as BMW AG integrating gesture-based controls into vehicle infotainment systems to improve driver safety and convenience. These systems utilize 3D cameras and radar sensors to detect hand movements, reducing the need for physical buttons and touchscreens.
Looking ahead, the next few years are expected to bring further breakthroughs in energy-efficient sensor design, edge AI processing, and seamless connectivity with Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. The proliferation of open-source development kits and standardized APIs is likely to accelerate innovation, enabling a broader ecosystem of developers to create custom gesture-based applications for smart homes, industrial automation, and assistive technologies.
Long-term, wearable gesture recognition systems are anticipated to become integral to ambient computing environments, where intuitive, touchless interaction is the norm. As privacy and data security concerns are addressed through on-device processing and encrypted communication protocols, adoption is projected to expand rapidly, with the potential to reshape how humans interact with digital and physical worlds across personal, professional, and public domains.
Sources & References
- Apple Inc.
- Ultraleap
- Noitom Ltd.
- Xsens Technologies
- Microsoft Corporation
- ProGlove
- STMicroelectronics
- Analog Devices
- Bioservo Technologies
- Infineon Technologies
- Qualcomm
- NVIDIA
- Immersion Corporation
- Bluetooth SIG
- IEEE
- Apple
- Microsoft
- Meta Platforms, Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Fitbit
- IEEE
- Bluetooth SIG
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- HaptX Inc.